Deploying OSPFv2 & OSPFv3
This Lab has been topology to configure OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 on Cisco
Routers and to advance of OSPF routing.
This Lab is broken-down:
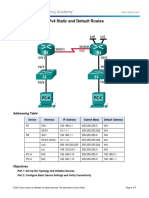
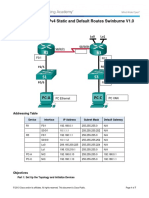
Link Address
OSPFv2
OSPFv3
OSPF Security
OSPF Optimization
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
�Link Addressing
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
�Deploying OSPFv2
Router 1 OSPFv2
Router 2 OSPFv2
Router 3 OSPFv2
Router 4 OSPFv2
Router 5 OSPFv2
Router 6 OSPFv2
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� Deploying OSPFv2
Deploying OSPFv2 on Router, Show Routing Neighbor,Routing Link-
State Database and Show Routing Table.
Router 3 OSPFv2 Neighbor
Router 2 OSPFv2 Link-State
Database
Router 5 OSPFv2 Link-State
Database
Router 3 OSPFv2 Routing
Table
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� Deploying OSPFv2
Deploying OSPFv3 on Router, Show Routing Interface, Routing
Neighbor, Routing Table.
Router 1 OSPFv3 Interface
Router 3 OSPFv3 Interface
Router 4 OSPFv3 Neighbor
Router 6 OSPFv3 Routing
Table
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� OSPF Security Authentication
OSPF Security Authentication on Router, Enable MD5
Authentication, Set MD5 Key ID and Password. Enable IPsec
Authentication, Set SPI and Password .
-> Enable MD5 Authentication
-> Set MD5 Key ID and password
-> Enable IPsec Authentication, set SPI and password
-> Enable MD5 Authentication
-> Set MD5 Key ID and password
-> Enable IPsec Authentication, set SPI and password
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� OSPF Optimization
OSPF Optimization on Router, Use BFD for all OSPF Interfaces,
Enable Prefix Suppression, ISPF, Enable LFA, Tunnel LSA Group
Pacing, Tune SPF Throttling Timers, and Tune LSA Throttling
Timers.
-> LSA
-> LSA
-> BFD
-> BFD
-> Prefix Suppression
-> Prefix Suppression
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� Test Ping IPv4
Test Ping IPv4 VPCS to Router. ping of IP Router, R1, R2, R3, R4,
R5 and R6.
Ping to R1's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1,
type ping 10.0.0.1 -c 5
Ping to R2's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1,
type ping 10.0.0.2 -c 5
Ping to R3's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1,
type ping 10.0.0.3 -c 5
Ping to R4's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1,
type ping 10.0.0.4 -c 5
Ping to R5's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1,
type ping 10.0.0.5 -c 5
Ping to R6's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1,
type ping 10.0.0.6 -c 5
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� Test Ping and Traceroute IPv4
Ping IPv4 and Traceroute, VPCS1, VPCS2, VPCS3, VPCS4.
Ping to VPCS2, in the
terminal of VCPS1, type
ping 10.2.2.2 -c 5
Traceroute to VPCS2, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type
traceroute 10.2.2.2
Ping to VPCS3, in the terminal of
VPCS1, type ping 10.2.5.2 -c 5
Traceroute to VPCS3, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type
traceroute 10.2.5.2
Ping to VPCS4, in the terminal of
VPCS1, type ping 10.2.6.2 -c 5
Traceroute to VPCS4, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type
traceroute 10.2.6.2
Traceroute to VPCS4, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type
traceroute 10.2.6.1
As we observed from above traceroute to VPCS 4 (10.2.6.2) and R6's LAN interface (10.2.6.1),
although both destination addresses belong to the same subnet, but due to 10.2.6.0/24 is an ECMP
(Equal-Cost Multi-Path) route with 2 next-hops (R3 and R4), and ECMP forwarding for IPv4 is
enabled by default in Cisco IOS, so both next-hops are installed into the router's forwarding table.
When destination addresses are not the same, R1 might forward them via different path for load
sharing purpose.
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com
� Test Ping and Traceroute IPv6
Ping and Traceroute IPv6. Ping to Router and Ping to VPCS
Ping to R1's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1, type ping
2001:DB8::1 -c 5
Ping to R2's Loopback,
in the terminal of VPCS1, type ping
2001:DB8:2 -c 5
Ping to VPCS2, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type ping
2001:DB8:2:2::2 -c 5
Traceroute to VPCS2, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type
traceroute 2001:DB8:2:2::2
Ping to VPCS3, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type ping
2001:DB8:2:5::2 -c 5
Traceroute to VPCS3, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type
traceroute 2001:DB8:2:5::2
Ping to VPCS4, in the
terminal of VPCS1, type ping
2001:DB8:2:6::2 -c 5
As we observed from above traceroute to VPCS4 (2001:DB8:2:6::2) and R6's LAN interface
(2001:DB8:2:6::1), although both destination addresses belong to the same prefix, but due to
2001:DB8:2:6::/64 is an ECMP (Equal-Cost Multi-Path) route with 2 next-hops (R3 and R4), and ECMP
forwarding for IPv6 is enabled by default in Cisco IOS, so both next-hops are installed into the router's
forwarding table. When destination addresses are not the same, R1 might forward them via different path
for load sharing purpose.
+6285693811614 fathinnaufal.13@gmail.com