HADOOP INSTALLATION GUIDE
Name: Fazal Rahim Daftani
Roll.No: 1272241004
Teacher: Veshal Pawar
Step 1: Install Java Development Kit
To start, you'll need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK) on your Ubuntu system. The
default Ubuntu repositories offer both Java 8 and Java 11, but it's recommended to use Java
8 for compatibility with Hive. You can use the following command to install it:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
Copy
Step 2: Verify Java Version
Once the Java Development Kit is successfully installed, you should check the version to
ensure it's working correctly:
java -version
Copy
Output:
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 3: Install SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is crucial for Hadoop, as it facilitates secure communication between
nodes in the Hadoop cluster. This is essential for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality
and enabling efficient distributed data processing across the cluster:
sudo apt install ssh
Copy
Step 4: Create the Hadoop User
You must create a user specifically for running Hadoop components. This user will also be
used to log in to Hadoop's web interface. Run the following command to create the user and
set a password:
sudo adduser hadoop
Copy
Output:
2/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 5: Switch User
Switch to the newly created 'hadoop' user using the following command:
su - hadoop
Copy
Step 6: Configure SSH
Next, you should set up password-less SSH access for the 'Hadoop' user to streamline the
authentication process. You'll generate an SSH keypair for this purpose. This avoids the need
to enter a password or passphrase each time you want to access the Hadoop system:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Copy
Output:
3/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 7: Set Permissions
Copy the generated public key to the authorized key file and set the proper permissions:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 640 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Copy
Step 8: SSH to the localhost
You will be asked to authenticate hosts by adding RSA keys to known hosts. Type 'yes' and
hit Enter to authenticate the localhost:
ssh localhost
Copy
Output:
4/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 9: Switch User
Switch to the 'hadoop' user again using the following command:
su - hadoop
Copy
Step 10: Install Hadoop
To begin, download Hadoop version 3.3.6 using the 'wget' command:
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.6/hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz
Copy
Once the download is complete, extract the contents of the downloaded file using the 'tar'
command. Optionally, you can rename the extracted folder to 'hadoop' for easier
5/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
configuration:
tar -xvzf hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz
mv hadoop-3.3.6 hadoop
Copy
Next, you need to set up environment variables for Java and Hadoop in your system. Open
the '~/.bashrc' Could you file in your preferred text editor? If you're using 'nano,' you can
paste code with 'Ctrl+Shift+V,' save with 'Ctrl+X,' 'Ctrl+Y,' and hit 'Enter':
nano ~/.bashrc
Copy
Append the following lines to the file:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
export HADOOP_HOME=/home/hadoop/hadoop
export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$HADOOP_HOME/bin
export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native"
Copy
Output:
6/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Load the above configuration into the current environment:
source ~/.bashrc
Copy
Additionally, you should configure the 'JAVA_HOME' in the 'hadoop-env.sh' file. Edit this file
with a text editor:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
Copy
Search for the “export JAVA_HOME” and configure it .
JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
Copy
Output:
7/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 11: Configuring Hadoop
Create the namenode and datanode directories within the 'hadoop' user's home directory
using the following commands:
cd hadoop/
mkdir -p ~/hadoopdata/hdfs/{namenode,datanode}
Copy
Next, edit the 'core-site.xml' file and replace the name with your system hostname:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
Copy
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value>
8/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
</property>
</configuration>
Copy
Output:
Save and close the file. Then, edit the 'hdfs-site.xml' file:
Next, edit the 'hdfs-site.xml' file and replace the name with your system hostname:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
Copy
Change the NameNode and DataNode directory paths as shown below:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>1</value>
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 9/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/namenode</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/datanode</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Copy
Output:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 10/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Save and close the file. Then, edit the 'mapred-site.xml' file:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
Copy
Make the following changes:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/home/hadoop/hadoop/bin/hadoop</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/home/hadoop/hadoop/bin/hadoop</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/datanode</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Copy
Output:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 11/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Finally, edit the 'yarn-site.xml' file:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml
Copy
Make the following changes:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Copy
Output:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 12/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
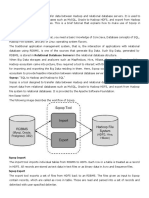
Step 12: Start Hadoop Cluster
Before starting the Hadoop cluster, you need to format the Namenode as the 'hadoop' user.
Format the Hadoop Namenode with the following command:
hdfs namenode -format
Copy
Output:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 13/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Once the Namenode directory is successfully formatted with the HDFS file system, you will
see the message "Storage directory /home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/namenode has been
successfully formatted." Start the Hadoop cluster using:
start-all.sh
Copy
Output:
You can check the status of all Hadoop services using the command:
jps
Copy
Output:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 14/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 13: Access Hadoop Namenode and Resource
Manager
First, determine your IP address by running:
ifconfig
Copy
If needed, install 'net-tools' using:
sudo apt install net-tools
Copy
To access the Namenode, open your web browser and visit http://your-server-ip:9870.
Replace 'your-server-ip' with your actual IP address. You should see the Namenode web
interface.
Output:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 15/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
To access the Resource Manager, open your web browser and visit the URL http://your-
server-ip:8088. You should see the following screen:
Output:
Step 14: Verify the Hadoop Cluster
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 16/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
The Hadoop cluster is installed and configured. Next, we will create some directories in the
HDFS filesystem to test Hadoop. Create directories in the HDFS filesystem using the
following command:
hdfs dfs -mkdir /test1
Copy
hdfs dfs -mkdir /logs
Copy
Next, run the following command to list the above directory:
hdfs dfs -ls /
Copy
You should get the following output:
Also, put some files into the Hadoop file system. For example, put log files from the host
machine into the Hadoop file system:
hdfs dfs -put /var/log/* /logs/
Copy
You can also verify the above files and directories in the Hadoop web interface. Go to the
web interface, click on Utilities => Browse the file system. You should see the directories you
created earlier on the following screen:
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 17/18
�11/30/24, 2:56 PM Hadoop Installation Guide
Step 15: To Stop Hadoop Services
To stop the Hadoop service, run the following command as a Hadoop user:
stop-all.sh
Copy
Output:
In summary, you've learned how to install Hadoop on Ubuntu. Now, you're ready to unlock
the potential of big data analytics. Happy exploring!
https://kongu.edu/support/hadoop/index.html 18/18