Example Exam Questions / MID_I
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
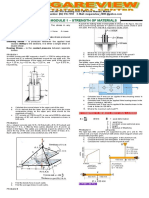
�Problem
The horizontal 25 kN forces are applied to pin B of the assembly shown. Knowing that a pin
of 20 mm diameter is used at each connection,
(a) Determine the maximum value of the average normal stress in links AB and BC.
(b) Determine the average shearing stress in the pin at C and the average bearing
stresses at C in member BC and at B in member BC.
Figure
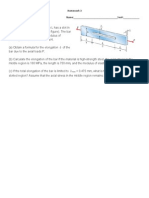
�Problem
An assembly of an aluminum tube (E = 70 GPa, A = 500 mm2) and a spring (k = 18 kN/mm)
is shown in Figure (2). A concentric load (9 kN) is applied at the midpoint of the tube.
Compute the reaction at A due to the load, in combination of a decrease in temperature of
45 oC in the aluminum tube. The coefficient of expansion α = 21.6 x 10-6 / oC. Note: spring is
not effected by temperature change.
Figure
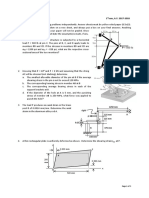
�Problem
The rigid bar is pinned at O and attached to two vertical rods BD and CE. Detailed information about the system is given in
Figure 1. Weight of the bar is negligible. Assuming that the rods are initially stress-free, what is the largest load P that can
be applied without exceeding stresses of 200 MPa in the steel rod and 60 MPa in the brass rod?
Calculate the strain in steel and brass rod. (30p)
Figure
Problem
A hollow circular pipe supports a load PA = 7800 N, which is uniformly distributed around a
cap plate at the top of the lower pipe. A second load PB is applied at the bottom. The inner and
outer diamters of the upper and lower parts of the pipe are; d1 = 51 mm, d2 = 60 mm, d3 = 57
mm, and d4 = 63 mm,respectively. The upper pipe has length L1 = 350 mm; the lower pipe
length is L2 = 400 mm. (Neglect the self-weight of the pipes)
Determine the PB so that the tensile stress in upper part is 14.5 MPa.
Figure
�Problem
A pick up track tailgate supports a crate (WC = 667 N). The tailgate weighs WT = 265 N and is
supported by two cables (only one is shown in figure). Each cable has an effective cross-
sectional area Ae = 11 mm2.
(a) Find the tensile force T and normal stress σ in each cable.
(b) If each cable elongates δ = 0.25 mm due to the weight of both crate and tailgate, what
is the average strain in the cable?
Figure
�Problem
Two plates with a 25 cm width and 20 mm thickness are joined together with two 12 mm thick
plates. Eight bolts with a 20 mm diameter in every side of the plates are used as shown in Figure
(2). If the plates are under a force of P=72 kN, determine
(a) Shearing stress on bolts. [10 points]
(b) The normal stress at sections 1-1, 2-2, 3-3, and 4-4 of the 20 mm thick plate. [10 points]
(c) The normal stress at sections 1-1, 2-2, 3-3, and 4-4 of the 12 mm thick plate. [10 points]
(d) The bearing stress at 20 mm thick plate. [5 points]
Hint: Assume every bolt carries equally one eighth of the force applied.
Important: Draw free body diagram in every step of the analysis or you will loose points even
if you have got the correct results.
43 2 1
P P
20 mm thick 43 2 1 12 mm thick
plates plates
P P
Figure