0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 17 views9 pagesSodaPDF-merged-Merging Result
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
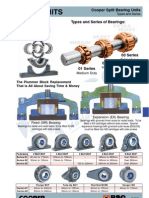
COCPER�INTRODUCTION
Reet mao)
Cee inom OOhrs
Cooper Bearings Group has an
worldwide presence, with sales
offices in the UK, USA, China, India
Cake ae a Aan aN ol
Ce gee Ree ans
Cee eo ea
Coli cia are ccoato (6)
Clamping Ring —>p
Inner Race
Ree
Peo o)
<< Shaft
COUPER�‘The following is a typical assembly sequence of a pillow block
cr flange mounted bearing and is included to allow engineers.
sing this catalog to uncerstand the assembly process of |
‘the Cooper bearing and to allow them to produce relevant
documentation for their own machines, which may require
‘his information. A full set of assembly instructions is usually
packaged with each standard bearing for use by the fiers.
If non-standard bearings are to be used, andar a ciferent
assembly sequence is required fer the application, specific
assembly instructions can be supplied on request.
‘The illustrations use a pillow block mounted unit as an
example,
Preliminary Notes
Bearings must be cisassembied before assembling into postion
Unwrap the bearing parts, remove the outer race halves (i
supplied assembled around other parts), and separate the
halves of the cage (ifrequired). Various cage jointing methods,
are used depending on size and series of bearing. Undo the
camping ring serews and remove the clamping rings from the
Remove the preservative from all surfaces of all the parts.
AA bearing and housing components (with the exception of
pressed steel die cast and plastic cages) are marked with
matching numbers or letters on each haf. Insure that the
atch marks on the halves are the sare and are placed
‘together on each component when the bearing is assembled
Even though cage halves are nat necessariy match-marked,
‘they must not be mixed, as the rollers are graded into sets.
‘Complete roller bearings are interchangeable between
similar Cooper cartridges. Individual parts should not be
interchanged. Cartridges are interchangeable between
standard cuter housings provided that standard clearances are
specified,
Step | — Housing Base
Piace the pillow block base or flange lower half into position. If
‘the precise location of the housing is predetermined it may be
bolted into position, Generaly pillow block bases may recuire
slight movement at a later stage in order to accurately position
the shaft
ete The plow Bek ae nt ahow rat of te eer tha fl fr ary of
hr eae
Step 2 — Inner Race
Lightly ol the shaft with thin machine oll zhen remove the
‘excess with a clean wiper: Place the inner race at the correct,
position on the cleaned shaft. Soft packing on the joint faces,
‘or feeler gauges, should be used to insure that the joint gaps
are approximately equal. Inner races of expansion bearings
are usualy set centrally with the outer race, but in cases of
significant axial expansion there may be a deliberate offset.
(This is usually up to a maximum of 10% of the roller length,
but may be more in the case of special types of bearing),
COCPER
139�Step 3 — Clamping Rings
Fit the clamping rings with joints at approximately 90° to the
inner race joints (45° in the case of large bearings with 4part
clamping rings). Progressvely tighten all damping rng serews.
Tap down each haf ofthe inner race and clamping rings
all around the shaft using a soft-faced hammer, or insert a
hardwood block between a steel hammer and the bearing parts
Retighten the clamping ring screws. Repeat until screws remain
fully ign. Tightening torques are listed on pages 163 to 167.
‘Check that there are approximately equal gaps at both joints of
the inner race.
(Check that there are approximately equal joints at both (or all
4) joints of each clamping ring
Step 4 — Cage and Rollers
‘Coat the bore of the cage and roll assembly with grease and
lightly cover the inner race assembly (fitted to the shaft) all
cover with grease for protection.
Assemble the cage (complete with rollers) around the inner
race. The two halves of the cage are fixed together by various
means depending on size and series of bearing. (Further details
are to be found in the assembly leaflets supplied with the
bearing, or details of the joint of a particular size and series of
cage can be supplied on request)
Step 5 - Cartridge and Outer Race Sub-Assembly
Place the half outer race with the lubrication hole in the top
half of the cartridge and the second half outer race into the
lower half of the cartridge. Insure that the ends of the outer
race project from the cartridge joint face by equal amounts.
All lipped outer races must be clamped axially, Side screws ‘A’
are filled to all GR cartridges. Side rods’B' are ftled to some.
szes only,�Radial screws'C’ and washers are ited to both EX and GR
cartridges of larger sizes onl
EX Careridges:
Just enter radial serews'C (where fitted, complete with
washers) into the corresponding outer race holes, but do not
tighten, Place the two half cartridges together complete with
half outer races, and filly tighten the joint screws D'. Fully
tighten the racial serews
Cartridges for Lipped Outer Races (GR and Special Types):
Just enter radial screws'C’ (where fitted, complete with
washers) into the corresponding outer race holes, but do not,
lighten. Place the two half cartridges together complete with
‘outer races, and full tighten the joint screws'D'. Enter the
side rods'8' (where fited) and side serews'A’. Progressively
‘and full tighten the side screws ‘A’ and radial screws ‘C’ (where
fitted).
All types:
Inject grease to fil the grease passages. Remove joint screws
‘D and separate cartridge halves, taking care that the outer
race halves do not fall out of position in their respective half
cartridges,
Step 6 — Seals
Ifthe unit i to be fitted with aluminury triple labyrinth (ATL)
seals, ft them onto the shaft as follows:
Separate the ATL seal halves by driving out the two jointing
pins. Lubricate the'O’ rings in the bore with grease.
Reassemible on the shaft by compressing the ©’ rings of both
halves sufficiently to allow the jointing pins to be reinserted,
and reinsert the pins. Note: ATL seals are able to slide along
the shaft once assembled
16!
Felt seals should be soaked in oii before fitting into the
cartridge end bores, Most types of seal other than triple
labyrinth seals and SRSRP seals are fitted into the cartridge end
bores before assembling the cartridge into positon.
Step 7 — Lubrication
‘Coat the inside of the cartridge, cage and rollers and all seals
‘with grease (See page 168 to 172 for correct quantity). For
speeds aver 150,000mm dn (shaft dameter in mn multiplied
by shaft speed in ram) approximately 40% of the grease used
should be applied to the bearing parts and the remainder
applied to the inside of the cartridge. This is to avoid excessive
curing of grease wren running at high speed.
COCPER�Step 8 — Cartridge
Lubricate the spherical seating of the bottom half of the
cartridge wih grease.
Place the bottom hatf of the cartridge on top of the bearing
and rotate 180° into the pilow block base or hal-fange.
Place the top half ofthe cartridge on top of the bottom half
close the cartridge and fully tighten the joint serews. Lubricate
‘the spherical seating with grease
Step 9 — Housing
I not already done, tighten the bolts fxing the pilow block
base or lower flange half into postion,
Place the pillow block cap or flange top half into pesition, Ifit
is safe to do so, running the shaft fora time without the outer
housing joint screws fully tightened wil help the bearing to
accurately align
Fully tighten the joint screws.
COCSPER�COMPARISON OF SERIES
For most shafl sizes Cooper offers a range of three standard
01 Series for medium duties
02 Series for heavy cuties
(03 Series for extra heavy duties
Inthe range I'l" to 4" the O1 Series is superseded by the
OLE Series of increased capacity, but with matching envelope
dimensions.
For certain bore sizes in the range 25x" to 6" Cooper also
coffer the 100 Series. This has slightly lower capacity than
(| Series but is mare compact and capable of higher speed
operation
‘The 04 Series is a specialized range of high speed bearings
available in a restricted range of bore sizes from 6 inches to
150mm,
Bearing references contain the series dentition as the prefix
numbers in the designation, eg,
01 B 415M EX
02 B 415M EX
are bearings of 0! & O2 Series respectively,
High Speed, Compact Bearing Medium Duty Bearing
together by bore size.This allows you to compare the capacity,
and speed capabilites in order to select the most appropriate
Generally if conditions allow and a satisfactory life is
theoreticaly achieved by 01/0|E bearings, this series of bearings
is the most economical series to select. The 02 and 03 Series,
are successively higher rated, bul are also more expensive in
terms of rst cost IFhigh speeds and/or restricted envelope
cimersions preclude the use of 01/01E Series, the 100 Series
should be selected if other conditions allow.
In the case of an existing bearing being replaced, there may
have been other factors than just load capacity involved in
the selection of the original bearing, itis often unnecessary to
‘match load capacities of exsting bearings to achieve satisfactory
bearing life. Wherever possile, the loads on existing bearings
should be assessed, This will insure the most appropriate anc
‘economical selection of Cooper bearings to realace them,
Cooper can assist with this selection
03 Series
Heavy Duty Bearing Extra Heavy Duty Bearing
COCSPER�JOINT GAPS AND INTERNAL CLEARANCES
Inner Race Joint Gaps
When the inner race is assembled around a shaft there should
be a small gap at both joints The gaps at the joints, typically
between 0.015” and 0.025" per side, ensure contact between
‘the bore of the inner race and the shaft This is ilustrated
below,
Selection of Internal Bearing Clearance
Gn represents the standard diametral clearance between
the rollers and the outer race specified by the International
Standards Organisation (SO) and is usually adequate between
-A°F and 212°F and when the temperature difference between
the shaft temperature and the housing temperature is less than
ms
C2 clearance is less than standard and is used for reciprocating
applications or when the shock loads and other conditions
demand reduced clearance.
Its limited to a temperature difference of 30°F between
shaft and housing temperature since high temperalures cause
‘expansion of the bearing components
C3 clearance is greater than standard and is typically used
‘when the difference between the shaft and bearing housing
surface temperatures is between 72°F and 130°,
CS is typically he greatest clearance that Cooper offers. It
is used when the difference between the shaft and bearing
housing surface temperatures is greater than 130°C.
Cooper does not typically offer a C4 clearance.
Radia load ratings listed inthis catalog are for standard
clearance and C2 bearings Bearings with C3 and C5 clearance:
have 5% and 10% lower capacity respectively
For most industrial applications zero clearance is not desirable,
Bearings will generate heat as they run. Without clearance,
bearings may bind and fail prematurely,
Wrong Correct
No contact between Fall contac between
Race and Shaft Race and Shaft
No z on
\
Inner Race
No gap Gap
COSPER�‘Cooper bearings are commonly supplied in two forms: the Fixed Type (‘GR’) and Expansion Type (‘EX’) as described below.
‘Where conditions are unsuitable for these standard types other configurations are possible, some of which are described on
pages 5 to 7.
Fixed Type Bearings (GR) ‘This type of bearing provides axial location to the rotating
portions of machinery and can sustain both radial and axial
‘The outer race of the fixed (GR) bearing has shoulders: loading
integral with the roller track, while the inner race assembly has
shoulders formed by hardened lips on the clamping rings or The inner race halves are accurately aligned by means of fitted
sila integral shoulders. camping rings.
GR Bearing (D Type) GR Bearing (C Type)
01 and 02 Series through 12°7/300mnm shalt size 01 and 02 Series through 12°/300mm shaft size
and 03 Series through 6"1155mm shaft size. and 03 Series through 6°/155mm shaft size.
100 Series al shaft sizes.
Expansion Type Bearings (EX) “The inner race is clamped to the shaft, and maves axially with
it when expansion or contraction occurs
‘The expansion (EX) bearing has a plain outer race roller track,
‘This bearing takes radial load only. ‘The Cooper expansion bearing offers virtually no resistance to
axial movement as the rollers spiral through the outer race
EX Bearing (D Type)
01 and 02 Series through 2°/200mm shaft ize
and 03 Series through 6"/15Smm shaft size.
100 Series al shaft sizes.
EX Bearing (C Type)
01 and 02 Series through 12°7300rm sha size
and 03 Series through 6'/155mm shaft size.
COSPER
You might also like
Instruction Manual For DODGE Setscrew, Eccentric Collar, D-Lok, H-E Series, E-Z Kleen, Ultra Kleen and Food Safe Mounted Ball Bearings
Instruction Manual For DODGE Setscrew, Eccentric Collar, D-Lok, H-E Series, E-Z Kleen, Ultra Kleen and Food Safe Mounted Ball Bearings
2 pages