1.
Program to demonstrate simple statements like printing the names (“Hello World”),
numbers, mathematical calculations, etc.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
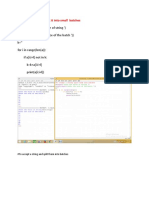
print("Hello World!")
#Output Hello
World!
#Mathematical Calculations
a = 20 b = 10
print("Addition:",a+b)
print("Subtraction:",a-b)
print("Division:",a/b)
print("Multiplication:",a*b)
print("Modulus:",a%b)
print("Power:",a**2)
#Output
Addition: 30
Subtraction: 10
Division: 2.0
Multiplication: 200
Modulus: 0
Power: 400
1
�2. Program to find all prime numbers within a given range.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
start=int(input("Enter number"))
end=int(input("Enter number"))
for n in range(start,end+1):
for i in range(2,n): if(n
%i)==0: break else:
print(n)
#Output
Enter number2
Enter number50
2
3
5
7
11
13
17
19
23
29
31
37
41
43
47
3. Program to print "n" terms of Fibonacci Series using Iteration
2
�Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
n=int(input("Enter the value of number"))
a=0 b=1
print("Fibbonacci series is ")
print(a) print(b) i=3
while(i<=n): c=a+b
print(c) a=b b=c
i=i+1
#Output
Enter the value of number10
Fibbonacci series is
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
13
21
34
4. Program to demonstrate the use of slicing in string.
3
�4. Program to demonstrate the use of slicing in string.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
s=str(input("Enter The String:"))
print(type(s))
print(s[0:3])#substring
s=str(input("Enter The String:"))
print(s[0:8:2]) s=str(input("Enter
The String:")) print(s[-1:-9:-1])
s=str(input("Enter The String:"))
print(s[-3:-6:-1])
s=str(input("Enter The String:"))
print(s[3:6])
#Output
Enter The String:computer
<class 'str'>
com
Enter The String:computer cmue
Enter The String:computer retupmoc
Enter The String:computer tup
Enter The String:computer
put
4
�5. Programs related to functions & modules
# Function with arguments
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
def fun_hello(name):
message="Hello "+name
return(message)
name=input("Enter your name ")
print(fun_hello(name))
#Output
Enter your name: Student
Hello Student
#Keyword argument
def sum(a,b,c):
return(a+b+c)
print("Sum is",sum(b=3,a=7,c=10))
#Output
Sum is 20
#Default argument
def welcome(str,address="Dhanaji Nana Mahavidyalaya,Faizpur"):
print("I am a ",str,"of ",address)
welcome(name="student")
#Output
I am a student of Dhanaji Nana Mahavidyalaya,Faizpur
5
�#Variable length argument
def vararg(*names):
print("Type of argument passed is",type(names))
print("The arguments passed are") for name in
names: print(name)
vararg("C","C++","Python")
#Output
Type of arguments passed is <class 'tuple'>
The arguments passed are
C
C++
Python
#Function with multiple return value
def getdimensions():
length=float(input("Enter The Length :-"))
width=float(input("Enter The Width :-"))
return length,width l,w=getdimensions()
print(l,w)
#Output
Enter The Length :-10
Enter The Width :-20
10.0 20.0
#Recursive function
def product(a,b):
if(a<b):
return product(b,a) elif(b!
=0):
return(a+product(a,b-1)) else:
return 0 a=int(input("Enter first
6
�number: ")) b=int(input("Enter second
number: "))
print("Product is: ",product(a,b))
#Output
Enter first number: 12
Enter second number: 4
Product is: 48
#User defined modules
def sq(n):
print("Square is", n*n)
import square
square.sq(5)
#Output
Square is 25
#Program to use math module
import math math.log10(10)
print(math.log10(10))
math.pow(2,3)
print(math.pow(2,3))
math.sqrt(100)
print(math.sqrt(100))
math.ceil(4.4875)
print(math.ceil(4.4875))
math.floor(5.6875)
print(math.floor(5.6875))
#Output
1.0
8.0
10.0
7
�6. Write a program that demonstrate concept of Functional Programming.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
# Lambda Function
area_square=lambda x: x*x #area of square is a^2
side=int(input('Enter a side value of square: '))
print(area_square(side))
#Output
Enter a side value of square: 5
25
#Mapping function
def square(n): return(n*n)
numbers=(1,2,3,4)
result=map(square,numbers)
print(list(result))
#Output
[1, 4, 9, 16]
#Lambda with filter
l=[1,2,6,9,4,12,7,8] a=list(filter(lambda
p:(p%2==0),l))
print(a)
#Output
[2, 6, 4, 12, 8]
#Lambda with reduce
from functools import reduce
l=[1,2,6,9,4,12,7,8] sub=reduce(lambda
a,b:(b-a),l)
8
�print(sub)
#Output
13
9
�7. Program to demonstrate the use of list & related functions.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B5
# Creating a list
l= ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date"]
print(l)
# Accessing elements in a list print("Second
Fruit:", l[1])
# Modifying elements in a list l[1]
= "grape"
print("Updated List:", l)
# Adding elements to a list l.append("kiwi")
print("List After Adding Kiwi:", l)
# Removing elements from a list
l.remove("cherry") print("List After
Removing Cherry:", l)
# Checking if an element is in the list
if "date" in l: print("Date is in List")
else: print("Date is not in the List")
# Finding the length of the list print("Number
of fruits in the List:", len(l))
# Sorting the list l.sort()
print("Sorted List:", l)
# Reversing the list l.reverse()
print("Reversed List:", l)
#Output
[‘apple’, ‘banana’, ‘cherry’, ‘date’]
Second Fruit: banana
10
�Updated List: ['apple', 'grape', 'cherry', 'date']
List After Adding Kiwi: ['apple', 'grape', 'cherry', 'date', 'kiwi']
List After Removing Cherry: ['apple', 'grape', 'date', 'kiwi']
Date is in List
Number of fruits in the List: 4
Sorted List: ['apple', 'date', 'grape', 'kiwi']
Reversed List: ['kiwi', 'grape', 'date', 'apple']
11
�8. Program to demonstrate the use of Dictionary & related functions.
#Creating Dictionary
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
D=dict({1:'odd',2:'even'}) print(D)
#Output
{1: 'odd', 2: 'even'}
#Accessing Values in Dictionary
D={'Name':'ABC','Age':22,'Subject':'Python'}
print("D['Name']:",D['Name'])
print("D['Age']:",D['Age'])
#Output
D['Name']: ABC
D['Age']: 22
#Traversing A Dictionary
D={'Name':'ABC','Age':22,'Subject':'Python'}
for i in D: print (i,":",D[i])
#Output
Name : ABC
Age : 22
Subject : 'Python'
#Update Dictionary
D={'Name':'ABC','Age':22,'Subject':'Python'}
D['Class']='SY BCA' print(D)
#Output
{'Name': 'ABC', 'Age': 22, 'Subject': 'Python', 'Class': 'SY BCA'}
#Remove Elements from Dictionary
D={'Name':'ABC','Age':22,'Subject':'Python'}
print(D.pop('Age')) print(D)
12
�print(D.popitem()) print(D) D.clear()
print(D) del D print(D)
#Output
22
{'Name': 'ABC', 'Subject': 'Python'}
('Subject', 'Python')
{'Name': 'ABC'}
{}
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "E:/Dictionary/remove.py", line 10, in <module>
print(D)
NameError: name 'D' is not defined
D={'Name':'ABC','Age':22,'Subject': 'Python'}
print(len(D)) #length() print(all(D)) #all()
print(any(D)) #any()
D1={'Name':'ABCD','Age':21,'Subject': 'Python'}
#print(cmp(D,D1)) #Compare x=D.get('Subject')
print(x)
#Output
3
True
True
Python
#Dictionary Methods
D={'Name':'ABC','Age':22,'Subject': 'Python'}
print(D.get('Age')) #get()
D1=D.copy() #copy()
print(D1) print(D.values())
#values print(D.keys())
#keys print(D.items())
#items
dict=dict.fromkeys(D) #Create New dictionary with keys
13
�print(str(dict)) dict=dict.fromkeys(D,5)
print(str(dict))
print(sorted(D.keys())) #sort functions
print(sorted(D.items())) D2={1:'one',2:'two',3:'three'}
print(sorted(D2.values()))
D.clear() #delete
print(D)
#Output
22
{'Name': 'ABC', 'Age': 22, 'Subject': 'Python'}
dict_values(['ABC', 22, 'Computer Science']) dict_keys(['Name',
'Age', 'Subject'])
dict_items([('Name', 'ABC'), ('Age', 22), ('Subject', 'Python')])
{'Name': None, 'Age': None, 'Subject': None}
{'Name': 5, 'Age': 5, 'Subject': 5}
['Age', 'Name', 'Subject']
[('Age', 22), ('Name', 'ABC'), ('Subject', 'Python')]
['one', 'three', 'two']
{}
14
�9. Program to demonstrate the use of Tuple.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
#Creating tuple
t=("DNM",'p',4,8,12) print(t)
#Output
(‘DNM’, 'p', 4, 8, 12)
#Deleting Tuple
t=("DNM",'p',4,8,12)
print(t) del t print(t)
#Output
(‘DNM’, 'p', 4, 8, 12)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 5, in <module>
NameError: name 't' is not defined
#Accesing the elements in Tuple t=("DNM",'p',4,8,12)
print(t[1],t[3],t[-1])
#Output p
8 12
#Tuples Operations t=("ABC","PQR","XYZ","GHI")
t1=("SHUBH","LABH","NMU")
print(t+t1) #Concatention
print(t*2) #Repetition if
"ABC" in t:
print("yes") #Membership for
x in t:
print(x) #Iteration
15
�#Output
('ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ', 'GHI', 'SHUBH', 'LABH', 'NMU')
('ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ', 'GHI', 'ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ', 'GHI',) yes
ABC
PQR
XYZ
GHI
#Built-in functions of Tuples
t1=(1,2,4,3,7,6,5) print(len(t1))
#Length
print("Any element are present in a tuple: ",any(t1)) #Any
print("Smallest element is: ",min(t1)) #Minimum
print("Largest element is: ",max(t1)) #Maximum print("Sorted
elements are: ",sorted(t1)) #Sort
print("Sum of all elements is: ",sum(t1))
#Output
7
Any element are present in a tuple: True
Smallest element is: 1
Largest element is: 7
Sorted elements are: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Sum of all elements is: 28
#Built-in Methods of Tuples
vowels=('a','e','i','o','i','a','u','i','u')
print("The count of i is:",vowels.count('i'))
print("The count of d is:",vowels.count('d'))
#Output
The count of i is: 3
The count of d is: 0
vowels=('a','e','i','o','u')
print("The index of i is:",vowels.index('i'))
#Output
The index of i is: 2
16
�10. Program to demonstrate the working of Class and Objects.
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
17
�Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
class customer:
def __init__(self):
self.id='C0121'
self.name="Priya"
self.city="Faizpur"
def putdata(self): print("Customer's
id is :",self.id); print("Customer's name
is :",self.name);
print("Customer's city is :",self.city);
def __del__(self):
print('Object destroyed')
c=customer(); c.putdata()
del c
#Output
Customer's id is : C0121
Customer's name is : Priya
Customer's city is : Faizpur
Object destroyed
18
�11. Program to demonstrate the working of Inheritance
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
class college: def detail(self):
print('College: '+'Dhanaji Nana Mahavidyalaya, Faizpur')
class stud(college):
def __init__(self):
self.rno=121
self.name="Riya"
self.course="BCA"
def putdata(self):
print("Roll No:",self.rno);
print("Name:",self.name);
print("Course:",self.course);
s=stud();
s.putdata()
s.detail()
#Output
Roll No: 121
Name: Riya
Course: BCA
College: Dhanaji Nana Mahavidyalaya, Faizpur
19
�12. Program to demonstrate the working of Overloading Methods
Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
class Area: def
find_area(self,a=None,b=None): if
a!=None and b!=None:
print("Area of Rectangle",(a*b))
elif a!=None: print("Area of
Square is",(a*a)) else:
print("Nothing to Find")
obj=Area() obj.find_area(30)
obj.find_area(10,20)
obj.find_area()
#Output
Area of Square is 900
Area of Rectangle 200
Nothing to Find
13. Program to demonstrate Exception Handling Mechanism
20
�Name:-Kundan Kishor Patil Div:- B
Roll no:- Date:- Batch no:- B4
try:
a=int(input('Enter first no:'))
b=int(input('Enter second no:'))
try: print(a/b) except
ZeroDivisionError as e:
print("You are trying to divide by zero") except
BaseException as obj:
print('Type of exception:',type(obj)) print('Type
of exception:',obj.__class__) print('Type of
exception:',obj.__class__.__name__) else:
print('You have entered correct input') finally:
print("Always executed")
#Output
Enter first no:12
Enter second no:0
You are trying to divide by zero
You have entered correct input
Always executed
#User defined exception
class Emp(Exception):
def __init__(self,msg):
self.msg=msg
21
�sal=int(input('Enter salary:')) mobileno=input('Enter Mobile
Number:') if sal<5000 or sal>70000 or len(mobileno)>10 or
len(mobileno)<10: raise Emp("Invalid salary or mobile number")
else:
print("Salary is:",sal)
print("Mobile number is:",mobileno)
#Output
Enter salary:56000
Enter Mobile Number:9987652436
Salary is: 56000
Mobile number is: 9987652436
22