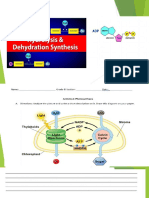
Calvin Cycle Notes
Overview
- Light-independent process of photosynthesis
- Takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts
- Powered by ATP and NADPH from light-dependent reactions
- Primary function: Convert carbon dioxide into three-carbon sugars
Three Stages of Calvin Cycle
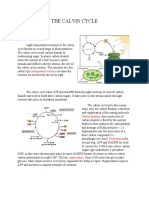
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Fixation
- CO2 from atmosphere combines with five-carbon ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)
- Creates a six-carbon compound
- Splits into two three-carbon molecules (3-phosphoglyceric acid)
- Enzyme RuBisCO catalyzes this reaction
2. Reduction
- 3-PGA molecules converted to glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate (G3P)
- Uses energy from ATP and NADPH
- NADPH donates electrons (reduction process)
- Converts light energy into long-term storage molecules like sugars
3. Regeneration
- Some G3P molecules create glucose
- Others recycled to regenerate RuBP
- Requires ATP
- Complex multi-step process
Key Characteristics
- Takes six turns of the cycle to produce one glucose molecule
- Consumes 18 ATP and 12 NADPH per glucose molecule
- Five out of six G3P molecules regenerate RuBP
- One G3P molecule becomes half a glucose molecule
Important Notes
- Each cycle turn "fixes" one carbon molecule
- Three turns create one glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate molecule
- Six turns allow two G3P molecules to combine into glucose
- Recycles ADP and NADP+ back to light reactions
Global Significance
- Critical process for converting atmospheric carbon into plant sugars
- Essential for creating structural materials like cellulose
- Enables plants to store energy from sunlight