0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views51 pagesMOM Lab
mechanics of materials lab
Uploaded by
himanshu.dps2005Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views51 pagesMOM Lab
mechanics of materials lab
Uploaded by
himanshu.dps2005Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 51
‘onal Institute of Technology Bhopal
of Mechanical Engineering
or Mechanics of Materials Lab
LAB MANUAL
_ MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
LAB
Maulana Azad National Institute of I chnology Bhopal
Department of Mecha: I Engineering
Lab Manual for Mechanics of taterials Lab
BUTM
— Study of impact testing and impact sirength
Determination of impact strength through Izod impact test
Determination of impact strength through Charpy impact test
| Study of hardness tests Ee A
Determination of Rockwell hardness for different materials
| Determination of Brinell hardness for different materials
Torsion testing of circular shafts
0. [Bending test on cantilever beam
Maulana Avad National Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechanical Engineering
—Lab Manual for Mechanics of Materials Lab
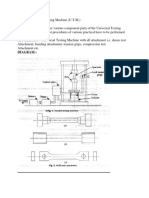
1. STUDY OF UNIVERSAL TESTING MACHINE
AIM: -
| Stady of Universal Testing Machine (U.T.M,)
| OBJECT: -
= To Shndy the 9 Bonus compondct pars of the Univer Testing Machine (U7-M. )& test
APPARATUS:
| Universal Testing
Procedures of various practical’s to be performed
Machine with all attachment ie, shears test attachment, bending attachment,
| tension grips, compression test attachment ete
THEORY : - The Universal Testing Machine consists of two units,
1) Loading unit,
2) Control panel,
LOADING UNIT:-
© It consists of main hydraulic cylinder with robust base inside. The piston which moves up
and down. The chain driven by electric motor which is fitted on left hand side.
The screw column maintained in the base can be rotated using above arrangement of chain,
Each column passes through the main nut which is fitted in the lower cross head.
The lower table connected to main piston through a ball & the ball seat is joined to ensure
axial loading.
There is a connection between lower table and upper head assembly that moves up and down
with main piston.
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechanical Engincering
__Lab Manual for Mechanics of Materials Lab od
* The measurement of this assembly is eartied out by number of bearings which slides over
ly oy
the columns,
* The test Specimen each fixed in the job is known as ‘Jack Job’. To fix up the specimen tightly,
the movement of jack job is achieved helically by the handle.
CONTROL. PANEL:-
It consists of an oil tank having a hydraulic oil level sight glass for checking the oil level.
B a hy¢ ight gl
The displacement-type piston pump has free plungers that ensure the continuation of high
pressure,
‘The pump is fixed to the tank from bottom,
The suction & delivery valve are fitted to the pump near tank Electric motor driven the pump
is mounted on four studs which is fitted on the right side of the tank.
‘There is an arrangement for loosing or tightening of the valve
The four valves on control panel control the oil stroke in the hydraulic system.
The loading system works as described below.
The return valve is close, oil delivered by the pump through the flow control valves to the
cylinder & the piston goes up.
Pressure starts developing & either the specimen breaks or the load having maximum value
is controlled with the base dynameters consisting in a cylinder in which the piston
reciprocates.
The switches have upper and lower push at the control panel for the downward & upward
movement of the movable head.
The on & off switch provided on the control panel & the pilot lamp shows the transmission
of main supply.
Azad National Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechanical Engineer i
Lab Manual for Mechanics of Materials Lab
UTM
© lstinent: Gefore tcating adjust the pend ith respect to capacity of the test ie. 8
‘nes; 10 Tones; 20 Tones; 40 Tones ete,
* For ex: A specimen of 6 tones capacity ‘gives more accurate result of 10 Tones capacity
Tange instead of 20 Tones capacity range
* These ranges of capacity are adjusted on the dial with the help of range selector knob. The
control weights ofthe pendulum are adjusted correctly
The ink should be inserted in pen holder of Tecording paper around the drum & the testing
Process is started depending upon the types of tests as mentioned below.
a
= —¥
‘Technology Bhop™!
ngineering
nal Institute of
Is Lab
Mechanical
anics of Mater!
a Azad Natio
Department 01
“Lab Manual for Mech
Maulan
MACHINE
UNIVERSAL TESTING
upper eros Head
space for Tens!
spacemen
Movable Cross Head
space for Compressive
spacemen
Load
Indicator
Speed
Control
TENSION TEST:-
# Select the pro
per job
job and complete upper and lower check adjust
istment. Apply so
me Greece
to the ta
spered surface of specimen or groove
\
* Then operate th
upper cross head
i rip operat
ecimen fully into the groove eration handle & grip the upper end of )
nd of test
|
a Azad National Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechan ering
_Lab Manual for Mechanics of Materials Lab
‘Then lock the jobs in this position by operating job working handle. Then open the left
control valve.
‘The printer on dial gauge at which the specimen breaks slightly return back & corresponding
Toad is known as breaking load & maximum load is known as the ultimate load.
IMPRESSION TEST:
* Fix upper and lower pressure plates to the upper stationary head & lower table respectively.
Place the specimen on the lower plate in order to grip.
+ Then adjust zero by lifting the lower table, Then perform the test in the same manner as
described in tension.
FLEXURAL OR BENDING TEST:-
Keep the bending table on the lower table in such a way that the central position of the
bending table is fixed in the central location value of the lower table.
The bending supports are adjusted to required distance.
Stuffers at the back of the bending table at different positions.
Then place the specimen on bending table & apply the load by bending attachment at the
upper stationary head.
‘Then perform the test in the same manner as described in tension test.
—
na A d National Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechanical Engineering
nual for Mechanics of Materials Lab
| Lab M.
b
| SHEAR TEST:- out
is i utter.
* Place the shear test attachment on the lower table, this attachment consists of c en
\De
oO!
* If the specimen breaks in two pieces then it will be in angle shear, & if it breaks in three
|
i 0 that
‘* The specimen is inserted in roles of shear test attachment & lift the lower table s« the
|
zero is adjusted, then apply the load such that the specimen breaks in two or three pieces.
Pieces then it will be in double shear.
| STUDY OF EXTENSOMETER:-
|
| This instrument is an attachment to Universal / Tensile Testing Machines.
|
| This measures the elongation of a test place on load for the set gauge length.
The least count of Measurement being 0.01 mm and maximum elongation measurement up
to3 mm.
‘This elongation measurement helps in finding out the proof stress at the required percentage
elongation.
8
‘ational Institute o ‘echnology Bhopal
chanical Engineering,
“chanics of Materials Lab
> TENSILE TEST ON UTM
Dstermine the Tensile Strength of
OBJECTIVE:
Azad N,
Department
of M
ab Manual f;
Limit of proportionality
Elastic limit
Gi) Yield strength
(iv) Ultimate Strength
©) Young’s modulus of elasticity
(vi) Percentage elongation
(vii) Percentage reduction in area,
APPARATUS:
@ Universal Testing Machine (UTM)
(ii) Mild steel specimens
(ii) Graph paper
(iv) Scale
Vernier Caliper
al
al Institute of Technology Bhop:
t nical Engineering
f Materials Lab _ 7
Jana Azad Nation
“ Department of Mechani
Lab Manual for Mechanic
Strain
Prarie Sted
‘THEORY:
‘© The tensile test is most applied one, of all mechanical tests.
+ In this test ends of test piece are fixed into grips connected to a straining device and to
a load measuring device
+ Ifthe applied load is small enough, the deformation of any solid body is entirely
elastic.
* An elastically deformed solid will retum to its original form as soon as load is
removed,
* However ifthe load is too large, the material can be deformed permanently.
* The inital part ofthe tension curve which is recoverable immediately after unloading
is termed,
* As elastic and the rest of the curve which rej
Presents the manner in which solid
“undergoes plastic deformation is termed plastic.
10)
PR
of
the
Maulana Azad National inet
Deparin ational Institute of Technology Bhopal
Lab Manu: ny of Mechanical Engineering
anual for Mechanics of Materials Lab
The stress below L
low which the def
leformations essentially entirely elastic is known as the
yield strength of material eee |
In some materi
pian 7 ial the onset of plastic deformation is denoted by a sudden drop in load
ing both an upper and a lower yield point. However, some materials do not |
exhibit a sharp yield point
—
° =. Plastic deformation, at larger extensions strain hardening cannot compensate
‘or the decrease in section and thus the load passes through a maximum and then
begins to decrease. |
This stage the “ultimate strength” which is defined as the ratio of the load on the
specimen to original erosssectional area, reaches a maximum value,
Further loading will eventually cause ‘neck’ formation and rupture.
PROCEDURE:
Measure the original length and diameter of the specimen. The length may either be length |
of gauge section which is marked on the specimen with a preset punch or the total length of|
the specimen.
Insert the specimen into grips of the test machine and attach strain-measuring device to it.
Begin the load application and record load versus elongation data.
Take readings more frequently as yield point is approached.
Measure elongation values with the help of dividers and a ruler.
Continue the test till a Fracture occurs.
By joining the two broken halves of the specimen together, measure the final length and
diameter of the specimen.
al Paee
Maulana Azad Natio
OBSERVATION:
() Initial diameter of specimen di ~
(6) Initial gauge length of specimen Lt =
| (©) Initial eross-seetion area of specimen Ai =
(@) Load of yield point Fi =
| (¢) Ultimate load after specimen breaking F =
| ( Final length after specimen breaking Lo
| (g) Diameter of specimen at breaking place d2 =
| @) Cross section rea at breaking place A2=
OBESERVATION TABLE:
Technology Bhopal
ineering
erials Lab
CALCULA
Uni
+ Ela
Load (N) | Original
Gauge
|
Length
{ ‘S.No
Extension
(mm)
Stress
(N/mm2)
+ Stes =o 0d £ ”
Sirin = ¢ = State tntenge |
‘original ength
+ Young's modulus E = S255. a
RECAUTIONS:
(©. The specimen stould be prepared in proper dimensions.
(©. The specimen should be properly to get between the jaws
© Take reading carefully
© Afer breaking the specimen, stop to mv.
[-Introduction:-
——
of Technology Bhopal
1 Engineering
s of Materials Lab______
na Azad National Institute ¢
of Mech:
anual for Mechanic:
LabM
NGTH
3, STUDY OF ACT-TESTING AND IMPA\ T STRE!
subjected to a sudden single aP|
plication,
st gives the material's behavior when
fated with a notch.
ial! chi
Iti also an excellent means to study the material's behavior under a sudden
‘The impact te
of load resulting in multi axils stress associ
ange in cross-
section.
This response of the material is
‘The basic objective ofthe impact test id evaluate the impact work, which is defined as the
x released when the material is subjected to a sudden force, and it is givena
called notched bar sensitivity.
amount of energ
unit (Nm)
‘The behavior of the ferric steel (low carbon, 0.001% carbons) under notched conditions can
be predicted from their properties as revealed by the tensile test, whereas the behavior of the
large group of non-ferrous metals and alloys and the austenitic ( high carbon 2%) carbon.
Mainly, the types of impact tests are usually performed are :
© Izod test: the impact load is applied to the cantilever with a notch at its base.
© Charpy test: the impact load strikes the center of a simply supported sample; the
sample is notched along of center of tension free.
pl
I Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechanical Engineer ing
Lab Manual for Mechanics of Material
a
Position of Specimen Vertical Horizontal
Direction of Netch-Fsce Hint ra i rom ser
weet Notch —Tviniouk V-Notch & U-Noteh
Size of Specimen 75mm x Form x 10mm 55mm x 10mm x 10mm
Type of Hammer Farming Hammer Ball in Hammer
Striking Point
Upper Tip of specimen Centre of specimen
Material Tested Metals and Plastics Metals
Kod Impact Test Charpy Impact Test.
as Page
ogy Bhopal
a Azad Nationa
Department of Mechan
Mi Mechanics
7
By IZOD TES
IMPACT STRENGTH OF STEEL
‘0 DETERMI
eel.
yf st
| |AIM: To determined impact strength o
| impact test
ine the impact strength of steel by Izod imps
} OBJECT: To determi
| -APPARATUS:
| 1. Impact testing machine
2. A steel specimen 75 mm X 10mm X 10mm
3. Vernier calipers
| + In manufacturing locomotive wheels, coins, connecting rods etc, the
| components are subjected to impact (shock) loads,
* These loads applied suddenly.
* The stresses induced in the components are many times more than
the stress produced by gradual loading
=
of Technology Bhopal
al Engineering
of Materials Lab
fupture and (jij) Notchimpact strength,
Two types
of notch impact tests are commonly
1. Charpy test
Src
10510558 mn
Seog ge
Lilli — re
ftom
recrecon
Im Izod test, the specimen is placed as cantilever beam. The specimens have V.
shaped notch of 45°. U-shaped notch is also common. The notch is located on
tension side of Specimen during impact loading,
| Pag
ulana Azad Nationa nei
Department of Mecha
+— ae ZOD
, NT DETAILS:
SPECIFICATIONS OF M/C AND SPE CIME!
Impact capacity=164 joules
| Least count of capacity (dial) seale =2
joules Weight of striking hammer =18 7kg.
Swing diameter of striking hammer
| =1600mm Angle of hammer before
striking=90? Distance between
i
supports=40mm
|
Striking velocity of hammer~5.6m/sec
Specimen size=75 mm X 10mm X
10mmType of notch = V- notch
Angle of notch =45° Depth of notch=2mm
PROCEDURE:
With the suiking hammer (pendulum) in safe test position, firmly
Hol i .
[old the steel specimen in impact testing machine’s vice in such away that th
at the
notchface t ar alf inside an above the top surface of the vice,
‘ace the hammer and is half inside and half. the top surface of th
agar
chnology Bhopal
ical Engineering
1 impact strength Nem or J
K = impact energy absorbed on Tepute N-m or J
A= area of cross section of specimen below the notch before test
mArea at V- notch, A=B X D
im a
Rreadth at V notch —B m
Depth at V-notch =D ....... om
The notch impact strength depends largely on the shape of the specimen and the
notch. The values determined with other specimens, therefore may not_be compared
with each other,
Impact strength of the given specimen is. Nem
Bring the striking hammer to its top most striking position unless it is
alreadythere, and lock it at that position,
Bring indicator of the machine to 2er0, or follow the instructions ofthe operating
manual supplied with the machine.
¢ of Technolog)
cal Engineer
‘of Materials Lab _
and break the specimen
y Bhopal
fs
ational Institut
tof Mechanit
for Mechanics
fall due to gravity
not absorbed by the specimen:
fier breaking the
a Azad N
Departme!
Lab Manual f
Release the hammer. It will
through its momentum, the total enerBY is
t its topmost height a!
‘Then it continues to swing: A\
endulum falls back. Note
specimen, the indicator stops moving, while the p*
the indicator at thattopmost final position
‘Again bring back the hammer to its idle position and back.
PRECAUTIONS:
‘The specimen should be prepared in proper dimensions
Take reading more frequently
Make the loose pointer in contact with the fixed pointer after the
pendulum Do not stand infront of swimming hammer or releasing
hammer
Place the specimen proper position
RESULT:
‘The energy absorbed for Mild Steel is found out to be- Joules.
T
al Institute of Technology Bhopal
chanical Engineering
‘s of Materials Lab__
1. Impact testing machine
2. A steel specimen 10 mm X 10mm X 55mm
EO)
“An impact test signifies toughness of material that is ability of material
to absorb energy during plastic deformation,
Static tension tests of unmatched specimens do not always reveal the
susceptibility of a metal to brittle fracture this important factor is
determined by impact test.
= Toughness takes into account both the strength and ductility of the
material.
Several engineering materials have to withstand impact or suddenly
applied loads while in service.
d to strengths achieved
erally lower as compare
Impact strengths are gen
aie
te of 0
| Engineering
Materials Lab
under slowly applied
ests are most extensively used, |
the notch bar t
fall types of impact tests,
‘Therefore, the impact test measures the enerBy necessary to fracture a
standard notch bar by applying an impulse load.
ial under shock loading
‘The test measures the notch toughness of mate!
Values obtained from these tests are not of much utility to design
problems directly and are highly arbitrary.
Still it is important to note that it provides a good way of comparing
toughness of various materials or toughness of the same material under
different condition.
This test can also be used to assess the ductile brittle transition temperature
of the material occurring due to lowering of temperature.
Mem
Ss
Spine
10% 10355 mn
Suing edge
Z, Dition
ame oftiow
(romsecton
22)
Azad National Institute of Technology Bhopal
Department of Mechanical Engineering
—__Eab Manual for Mechanics of Materials Lab
CHARPY
# L iD SPE CIMENT DETAILS: |
|
Impact capacity=300joules
Least count of capacity (dial) scale =2
Joules Weight of striking hammer =18.7kg
Swing diameter of striking hammer
=1600mm Angle of hammer before
striking=160° Distance between
supports=40mm
Striking velocity of hammer=5.6m/sec
Specimen size=55 mm X 10mm X
10mmType of notch = V- notch
Angle of notch =45°
Depth of notch=2mm
23 [Page
—————————
{
DESCRIPTION OF MACHINE:
nite oT ‘Technology Bhopal
engineering
Is Lab _
g machine consists of the robust frame, |
The pendulum impact testiny
lum, the specimen support and the
apa ngs.
The pendulum shaft is attend in anti-friction bearings
pendulum shaft.
measuring dial.
the pendul
The pendulum is clamped to
‘The pendulum consists of the pendulum pipe and the pendulum
hammer of U- shaped design.
Into this, the striker is mounted for conducting Charpy impact test.
The range, within which the pendulum is swinging, is partially
protected by the guard.
A latch is provided which keeps the pendulum is elevated position.
A lever is provided for operating the latch and releasing the
pendulum.
There is a dial attached concentrically with the pendulum shaft,
© scale is designed such that the pact energy absor'
The de ‘d such that th t ibsorbed in
=
b
reaking the specimen can be read directly in joules,
24 |
Maulana 4
Depa
Lab M
1 Nation,
al Institute of" |
(ment of Me
anual for Mec
py wnpac’ test
Fic. 7-4
Specimen o
|
PROCEDURE:
aa |
+ With the striking hammer (pendulum) in safe test position, firmly hold the
steel specimen in impact testing machines vice in such a way that the notch |
faces s thehammer and is half inside and half above the top surface of the |
|
vice.
Bring the striking hammer to its top most striking position unless it is already
there,and lock it at that position.
* Bring indicator of the machine to zero, or follow the instructions of the
operatingmanual supplied with the machine.
Release the hammer. It will fall due to gravity and break the specimen through
* Release :
its ‘entum, the total energy is not absorbed by the specimen.
its mom 5
25 |Page
aulana Azad Nationa Institute 0! Technology Bhopal
f y |
Ni 1 Ins' :
™ Department of Mechanical Engineering
ab Manual for M echanics of M rials Lab |
Lab M: panics of Mate!
- | «Then it continues toswing-
n, the indicator stops Moving, |
i « Atits topmost height after breaking the specime!
while the pendulum falls back.
«Note the indicator at that topmost final position.
} «The specimen is placed on supports oF anvil so that the blow of
hammeris opposite to the notch.
EVALUTION OF TEST:
‘The notch impact strength ‘I’ is calculated according to the following
relationI =
Where,
I= impact strength N-m or J
K = Impact energy absorbed on repute N-m or J
A
= are: ss Se
a of cross section of specimen below the notch before test
st
Area at V-notch, A=B X D
Breadth at V- notch = B
Depth at V- notch =p
26 |
a Aza ; ‘
aN a National tnstitute of 1 ‘echnology Bhopal
a aa me: hanical Engi
an ‘chanics of Mate
notch. The van
es determined with other specimens, therefore may not be compared
with each other.
_ Specimen should be Prepared in proper dimensions
Take reading more frequently
Make the loose pointer in contact with the fixed pointer after the
hammer
Place the specimen proper position
RESUL'
The energy absorbed for Mild Steel is found out to be- Joules,
ical Enginecring
Azad Ni
Materials Lab
Depart
Lab Manual f
Maulan
tof Mecha
Mechanics of
STUDY OF HARDNESS TI
ation or scratching,
softer or harder material depending on
Lintrodu
© Generally, hardness means the resistance to indent
«The material is classified according to its hardness (©
the indenter or the scratcher material.
© So, hardness is relative measurement depends on both testing and indenting materials,
‘According to the previous definition, if the indenter deforms the tested ms
aterial, we can say
that the indenter is harder than the tested material and if not, the indenter is softer than the
tested material.
‘© Innature, diamond is classified as the hardest material
+ The measurement of hardness test is classified mainly to three types:-
this type is roughly used nowadays and it depends on using a diamond,
1. Scratch hardness
This type is not suitable for metals
and : a
shapes. In this type, a static load is applied to the specimen for a period of time and th
indent oats a
lntion shape and dimensions are used to calculate the hardness numbers, Many ti
. Many tests are
Oa -
classified under this type such as: Brinell, Rockwell and Vickers hardness tests. These tests are
7 's. These tests
| 3: Rebound or dynamic hardness: - in this ’Pe, an indenter is dropped on the tested material
v1 ness: ty, i th
:
Maulan: Azad NX
Depar ‘tne,
Lab Man
Macro-hardness is used on 4
tional ins
nt of
Al for Mech:
ols, dies,
8 oF sn
titute
and sheet Material is
hardness is used on thin shege
all test materials that ma
hardness tests.
Macro-hardness is widely “Sed; and has with three methods:
The Rockwell hardness test, Vickers hardness test, and fin
main differences in these tes.
S are the size,
shape and the m:
hardness machine,
| I Tehas a large value of young's modulus of elasticity
2. Its surface is polished well
3. The operating condition is at moderated temperature
nics of Materials Lab
ing
in the heavier gages, while
'y Not respond accurately to Macro-
|
ally the Brinell hardness test. the
taterial used for the indenter in the
29| Page
nology Bhopal
gineering
ae
we tof Mech :
for Mechanics of Mate
Test of Mild Steel.
AIM:
using Rockwell hardness test, |
OBJECT: To determine the hardness of the given specimen
APPARATUS: 1. Rockwell hardness testing machine i
Pr
2. . Specimen of hard steel
a 1920.
i Rockwell test is developed by the Wilson instrument co USA in 7
This test is an indentation test used for smaller specimens and harder
materials. The test is subject of IS: 1586.In this test indenter is forced into
the surface of a test piece in two operations, measuring the permanent
inerease in depth ofan indentation from the depth increased from the depth
reached under a datum load due to an additional load. Measurement of
indentation is made after removing the additional load. Indenter used is the |G
cone having an angle of 120 degrees made of black diamond,
30]
Maulana Azag n,
tute of Technology Bhopal
nical E,
“fecha
Indenter 7
Flevating
serew
Hand wheel.
© Fix, 6 Rockwell hardness tester,
> Weights
TECHNICAL
Rockall HP,
Maximum test height: | 295mm.
I -
| Depth of throat: 150mm.
| I —
| Maximum depth of screw below base: | 280mm.
|
| Dimensions of machine:
[210 X 470mm.
850mm.
| Height:
|
- 125 kg
Net weight: al
LE
Se
ail
jeute of Technology Bhopal
cering.
1 Inst
aulana Azad N tion a a
Deparanent of LET eratl oe :
Lab Manual for Me o -
PROCEDURE:
adopted verycarefully:
For earying out tests, the following procedure should be
any negligence may lead damage to the indenter
ost according to the Rockwell scale required |
‘Adjust the weight on plunger of dash-p
asshown on chart. i
Keep the lever at position A.
Place specimen securely on testing table. Tur the hand wheel clockwise, SO that
specimen will push the indenter and show a reading on dial gauge as small pointer
at ‘3° (red spot ) and long pointer close to “0” of outer scale.
Tum the lever from position A to B slowly so that, the total load is brought into
action without any jerks.
The long pointer dial gauge reaches a steady position when indentation is complete.
‘Then take back the lever to ‘A’ position slowly (Sudden return to lever from B to A
my show erratic reading). The weights are thereby lifted off, only the initial load
remaining active.
6 Read the figure against the long pointer that is the direct reading of the Rockwi
ie figure against ig ing of th
ockwel
- ——
ore Ustitute of Tec!
€chanica|
Me
hnology Bhopal
| Engineeri
|. Thickness of the specimen
Should not be less than g times the depth of
center of indentation should be greater than 2.5 times diameter of indentation.
3. Rapid rate of applying load should be avoided. Load applied on the ball may rise
a Tittle because of its sudden action. Also rapidly applied load will restrict plastic
flow ofa material, which produces effect on size of indentation.
33] F
J SUNo| Specimen
| Material
TABULAR COLUMN: (
d Nation
ament of M
ral for Meeh
rat Institute of
nic
ROCKWELL TEST):
vechnology
incering
Bhopal
uab
oo Toad Rock —
Type of Loa‘ well
o
lie
indenter | indenter ne ; reading
a
(mm) (Ke) | PRAHRB/HR
CHART. Chart for most commonly used for Rockwell hardness test.
Total test force | 60ksi 100ks 150kef
preliminary -
test force
(10kgt) —_
Indicator Diamond Cone | Ball 1/16 Diameter Diamond — Cone
120° 120°
Scale |A IC \
Pointer position | Set Set Set
ol at | |
Dial to beread__| Black Red’ Black \
Typical Thin steel and Soft steel, S
ical : teel, hard cast
| application shallow case] malleable, steel, deep
hardened steel copper and | case hardened
aluminum alloys | steel, —_ others.
metals
\
hnology Bhopal
ngineering
* of Materials Lab
71 Institute of Tee
tor echanical BK
echan,
Take AVErABE OF five Valueg OF indentation of each specimen,
Obtain the hardnessmumiy,
from the dial of a machine,
Compare Brinell and Rog
‘kwell hardness tests obtained,
echnology Bhopal
ering
als Labo
ute of Tt
ical EI :
of Materi
al In:
lech
Department 0
Di f
Lab Manual for Mee}
st
8, BRINELL HARDNESS TEST
AL
ing Machine
nell test
To find hardness of the given specimen by Rockwell & Br
PARATUS:
1. Brinell Hardness testing machine
2. specimen of mild steel / cast iron/ non-ferrous metals and
3. Brinell microscope.
PRINCIPLE BRINELL TESTING:
Brinell hardness test is an indentation hardness test using a calibrated
machine to force a hard steel ball indenter under specified conditions of load
and name, into the surface of the material under test and to measure the
diameter of the resultingimpression after release of the load.
SPECIFICATION OF HARDNESS TESTING M/C AND INDENTORS
Maulana Azag x
Deparing,
Lab Manuay fo
Nnology Bhopal
ince
erials Lab
a Brinelleum- Rockwel) hardnes,
SS testing 4
m/e
i along
figure. Is specification ATE as Foto ‘0M& With the specimen is shown in
7 lows,
1. Ability to determing hardne,
ess
2 Diameter of ball (as indo
. eo) used
hardened steel all of specified diameter “D” mm under a given load “FN and measuring
the average diameter ‘d’ mm of the impression by a Brinell inicroscope. The Brinell
hardness HB is definedas the quotient of the applied force ‘F” divided by the spherical
area of the impression.
Brinell hardness, HB
Where,
F- Load. .N |
D= Diameter of the indenter .....-..-
mm Diameter of _ the
Impression.......++ mm
of Technology Bhopat
engineering
Sof Materials La Lab | _
nclosed design protects the inter, 1
al
on body. The ¢
ous elements. The main screw ig al
so
‘The hardness test is of cast 1"
ed dust and extrane
operating parts from determin
low. The basic system 1
ed on free end of lever, which transmit
.s of weights and levers. The Weight
s
protected by a rubber b
under hydraulic dash — pot time control are appli
ork -piece for determination of hardnes
8
the pressure.On plunger and there by on the we
f work — piece during the test which
value. A clampingdevice enable the tight clampit
at times can not be checked under normal conditions,
%E? Bracthonhes nee
Imes minder, BIW e——_2
Dip
38
“chnology Bhopal
«
280mm,
Dimension of, machine: 210 X 470
mm.
Height: 850 mm.
Net weight: eke
PROCEDURE:
For carrying out tests, the following procedure should be adopted very carefully; any
indents
negligence may lead damage to the indenter.
Sir ar a
d er of dash — pot ‘ding to the Rockwell scale requires
ist the weights on plunger of dash — pot accor
. Adjust ‘ights on plung:
as shown on chart.
2. Keep the leaver at position A. cane wn
Jy on testing table. Tern the
3 Place specimen securely 0
cute 0 pechnolod: Bhopal
5 opainecring,
| , Poecea neice A
” Mecha of Materials Lab _
| for Meehan ies of N als. - 7
ab Manual f¢ spr and show # ro
enter of diameter
' bovine Clamp |
© Ws Stand
+ DatGage ||
§ Loge Pan
These | CANTILEVER TEST
IU Instita
chanical eng
MAN
Me of Technology Bhopal
Necring. department
ViNtehanics of materials
You might also like
- Civil Engineering Department Lab ManualNo ratings yetCivil Engineering Department Lab Manual47 pages
- Sir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualNo ratings yetSir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab Manual47 pages
- Saurav Mashidkar 4-B 249 (1) - CompressedNo ratings yetSaurav Mashidkar 4-B 249 (1) - Compressed30 pages
- Experiment No: - 11: Compressive Strength of BrickNo ratings yetExperiment No: - 11: Compressive Strength of Brick32 pages
- Materials Testing Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 1 Inspection of The Materials & Testing LaboratoryNo ratings yetMaterials Testing Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 1 Inspection of The Materials & Testing Laboratory10 pages
- Barkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnNo ratings yetBarkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation On20 pages
- 100 Electronic Projects With Circuit Diagram PDF97% (37)100 Electronic Projects With Circuit Diagram PDF105 pages
- Battery Management System (BMS) For Lithium-Ion Batteries100% (6)Battery Management System (BMS) For Lithium-Ion Batteries98 pages
- Battery Management Systems For Large Lithium Battery Packs (PDFDrive)100% (9)Battery Management Systems For Large Lithium Battery Packs (PDFDrive)303 pages
- Make Your Own Diagnostic Equipment Mandy Concepcion PDF96% (25)Make Your Own Diagnostic Equipment Mandy Concepcion PDF129 pages
- A Text Book of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines - R. K. Bansal77% (22)A Text Book of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines - R. K. Bansal1,129 pages
- Advanced Hybrid and Electric Vehicles System Optimization and Vehicle Integration by Michael Nikowitz100% (10)Advanced Hybrid and Electric Vehicles System Optimization and Vehicle Integration by Michael Nikowitz230 pages
- Power Electronics Devices and Circuits Second Edition PDF100% (20)Power Electronics Devices and Circuits Second Edition PDF383 pages
- Unit 1 PPT Introduction To Electric Vehicle75% (4)Unit 1 PPT Introduction To Electric Vehicle97 pages
- Tom Denton, Hayley Pells - Electric and Hybrid Vehicles-Routledge. Taylor & Francis Group (2024)100% (5)Tom Denton, Hayley Pells - Electric and Hybrid Vehicles-Routledge. Taylor & Francis Group (2024)260 pages