Last Part WC
Uploaded by
KriscismLast Part WC
Uploaded by
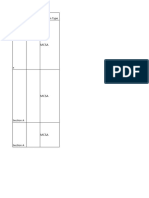
KriscismShaw Corporation is considering a plant expansion that will an increase in accounts receivable greater than a
increase its sales and net income. The following data B
decrease in inventory.
represents management's estimate of the impact the an increase in cash equal to a decrease in accounts
proposal will have on the company. C
receivable.
Current Proposal an increase in inventory equal to an increase in accounts
Cash $100,000 $120,000 D
payable.
Accounts payable $350,000 $430,000
Accounts receivable $400,000 $500,000 An acquisition takes places when a firm:
Inventory $380,000 $460,000 A combines with another firm to create a new firm.
Marketable securities $200,000 $200,000 buys another firm using debt to finance a significant
B
Mortgage payment (current) $175,000 $325,000 portion of the transaction.
Fixed assets $2,500,000 $3,500,000 C buys a controlling interest in another firm.
Net income $500,000 $650,000 D buys any percentage of ownership in another firm.
The effect of the plant expansion on Shaw's working capital
would be a(n) The XYZ Company buys all of the stock of the ABC
A decrease of $50,000. Company and the XYZ Company remains in existence after
the transaction. Which of the following is the best description
B decrease of $30,000.
of this transaction?
C increase of $30,000. A An acquisition
D increase of $120,000. B A merger
C A leveraged buyout
Under the current situation, the total current assets equal
$1,080,000 and total current liabilities equal $525,000, which D A spin-off
calculates working capital to be $555,000. Under the
proposal, the current assets equal $1,280,000 and the The KIO Company operates stores that sell women’s
current liabilities equal $755,000, calculating a working clothing and the ASW Company produces women’s clothing.
capital equal to $525,000. Given this, the effect of the plant The two companies decide to combine to form a new
expansion on Shaw's working capital is a decrease of company. Which of the following is the best description of
$30,000 ($555,000 − $525,000). this transaction?
A A conglomerate merger
Starrs Company has current assets of $300,000 and current B An acquisition
liabilities of $200,000. Starrs could increase its working C A vertical merger
capital by the: D A horizontal merger
A prepayment of $50,000 of next year's rent.
refinancing of $50,000 of short-term debt with long-term When two firms that make different parts used at different
B
debt. stages of the manufacturing process for the same finished
acquisition of land valued at $50,000 through the issuance good are combined, it is referred to as what type of merger?
C
of common stock. A Vertical merger
D purchase of $50,000 of temporary investments for cash. B An acquisition
C Conglomerate merger
Your firm has a quick ratio of 0.9 and a current ratio of 2.1. D Horizontal merger
Industry averages are 1.0 for the quick ratio and 2.0 for the
current ratio. Which of the following is true about the firm's The DIL Company operates candy stores and the BTX
working capital position? Company produces automobiles. The two companies decide
The firm has more accounts receivable than other firms in to combine to form a new company. Which of the following is
A
the industry. the best description of this transaction?
The firm has less accounts receivable than other firms in A An acquisition
B
the industry. B A vertical merger
The firm has more inventory than other firms in the C A horizontal merger
C
industry. D A conglomerate merger
The firm has less inventory than other firms in the
D
industry. When two firms are combined that are from different
industries, it is referred to as what type of merger?
Which one of the following would increase the working A Horizontal merger
capital of a firm?
B Vertical merger
A Cash collection of accounts receivable
C Conglomerate merger
Purchase of equipment financed by a 30-year mortgage
B D An acquisition
payable
C Cash payment of accounts payable
Refinancing of accounts payable with a two-year note
D
payable
Net working capital is the difference between:
When two firms in the same industry are combined, it is
A current assets and current liabilities.
referred to as what type of merger?
B fixed assets and fixed liabilities.
A Horizontal merger
C total assets and total liabilities.
B Vertical merger
D shareholders’ investment and cash.
C Conglomerate merger
A positive change in net working capital represents:
D An acquisition
an increase in fixed assets greater than a decrease in
A
cash.
The STQ Company and the BGT Company both sell
specialty glassware. The two companies decide to combine Which of the following is a strategy wherein a firm elects only
to form a new company. Which of the following is the best part of its board each year?
description of this transaction? A Golden parachute
A A horizontal merger B Poison pill
B A vertical merger C Leveraged recapitulation
C An acquisition D Staggered board of directors
D A leveraged buyout
The KGE Company is concerned that another company will
The XCV Company and the WER Company both sell try to acquire it. To reduce the likelihood of being acquired,
children’s clothing. The two companies decide to combine to KGE’s board of directors votes to elect only a portion of the
form a new company. Which of the following is the best board every year. What tactic has KGE used?
description of this transaction? A A voting rights plan
A An acquisition B The white knight defense
B A horizontal merger C A fair price provision
C A vertical merger D A staggered board of directors
D A conglomerate merger
The HRW Company is concerned that another company will
The AOW Company is concerned that the VBF Company try to acquire it. To reduce the likelihood of being acquired,
will try to acquire it. To reduce the likelihood of being HRW’s board of directors votes to borrow a large sum of
acquired by VBF, AOW tries to convince the DWQ Company money and pay that money out as a special dividend to
to outbid VBF. What tactic has AOW used? existing shareholders. What tactic has HRW used?
A A golden parachute A A golden parachute
B The white knight defense B The white knight defense
C A fair price provision C A leveraged recapitalization
D A staggered board of directors D A staggered board of directors
Which of the following provides very large payouts to Which of the following makes a firm less attractive to
executives released as part of an acquisition? acquiring firms by taking out a significant amount of debt and
A Leveraged recapitalization distributing large cash dividends to shareholders?
B Golden parachute A White knight defense
C White knight defense B Poison pill
D Staggered board of directors C Leveraged recapitalization
D Staggered board of directors
Which of the following is a defense against corporate
takeovers that still results in the firm being acquired by A publicly traded company is planning to divest its Division A
another firm? for $100 million. Private investors have pooled their capital of
A Golden parachute $10 million and plan to finance the balance of $90 million via
B Leveraged recapitalization debt financing with Division A's assets as collateral. The new
C White knight defense owners plan to give the new management a bigger stake in
the company by providing stock options. They also
D Poison pill
redesigned performance measures and incentive schemes
for employees to minimize inefficiencies and bureaucracy.
Making all debt redeemable in the event of a firm being This scenario most closely describes a
acquired is part of which type of defense against corporate *Source: Retired ICMA CMA Exam Questions.
takeover?
A management recapitalization.
A Golden parachute
B management buyout.
B Leveraged recapitulation
C leveraged recapitalization.
C White knight defense
D leveraged buyout.
D Poison pill
The HJG Company is concerned that another company will
try to acquire it. To reduce the likelihood of being acquired,
HJG’s board of directors votes to give executives huge Which of the following statements about leveraged buyouts
bonuses in the event HJG is acquired by another company. is not correct?
What tactic has HJG used? A leveraged buyout is less risky than other types of
A
A The white knight defense purchases.
B A golden parachute In a leveraged buyout, the assets of the company are
C A leveraged recapitalization B used as collateral for the loans needed to finance the
purchase.
D A voting rights plan
A leveraged buyout is often used when a company is
C
purchased by its management team.
The XRF Company is concerned that another company will
try to acquire it. To reduce the likelihood of being acquired, A leveraged buyout is often used to take a company
D
XRF’s board of directors votes to make all its debt private.
redeemable in the event it is acquired. What tactic has XRF
used? Which of the following would be the most likely benefit
A A golden parachute realized from a conglomerate merger?
B A leveraged recapitalization A Less reliance on outside suppliers
C A poison pill B Greater ability to dictate prices to customers
D A fair price provision C Economies of scale in production
D Greater diversification of product offerings
C A company becomes too large to manage.
Which of the following would be the most likely synergy D A company is trying to raise cash.
realized from a vertical merger?
A Greater ability to dictate prices to customers
B Less reliance on outside suppliers for raw materials Which of the following statements concerning spin-offs and
C Greater variety of product offerings equity carve-outs is correct?
D Lower production costs per unit In a spin-off shareholders of the existing company receive
A shares of the new entity but in an equity carve-out shares
Which of the following would be the most likely synergy in the new company are sold on the open market.
realized from a horizontal merger? In an equity carve-out shareholders of the existing
A Economies of scale in production B company receive shares of the new entity but in a spin-off,
B Greater diversification of product offerings shares in the new company are sold on the open market.
C Less reliance on outside suppliers Shareholders of the existing company receive shares of
C the new company in spin-offs and equity carve-outs. The
D Easier access to customers
difference is the percentage of shares distributed.
Which of the following would be the most likely benefit Shares in the new company are sold on the open market
realized from a vertical merger? D in spin-offs and equity carve-outs. The difference is the
percentage of shares distributed.
A Less reliance on outside suppliers
B Greater diversification of product offerings
C Economies of scale in production
There are four main divestiture options available to company:
D Lower variability in annual sales
spin-off, equity carve-out, tracing stock, and split-up.
Under which option or options is a new company created?
The AIK Company decides to issue a stock that is based on
A Spin-off, equity carve-out, and tracking stock
one of its most profitable business units. AIK retains
ownership of the entity, but the stock is sold on the open B Spin-off, equity carve-out, and split-up
market for cash. Which of the following is the best C Spin-off, equity carve-out, tracking stock, and split-up
description of this transaction? D Spin-off and split-up
A A spin-off
B An equity carve-out Which of the following statements concerning tracking stock
C A tracking stock and equity carve-outs is correct?
D A split-up A new entity is created with an equity carve-out, but a new
A
entity is not created when tracking stock is issued.
Which type of divestiture does not result in a new entity A company receives cash when tracking stock is created
being formed? B
but not with an equity carve-out.
A A spin-off A company retains control of the part of a business a
B An equity carve-out C tracking stock is based on but not the part of a business
C Tracking stocks an equity carve-out is based on.
D A split-up Shares in an equity carve-out are sold on the open market
D to any interested investor while tracking stock is sold to a
The QYU Company is broken up into the JIO Company and company’s existing shareholders.
POI Company. Shareholders of QYU exchange their shares Which of the following is least likely to be a reason for a
for shares in JIO and POI. Which of the following is the best company to do a split-up?
description of this transaction? A A company is trying to raise cash.
A A spin-off
B A company is trying to narrow its strategic focus.
B An equity carve-out
C A tracking stock A company is trying to avoid government and regulatory
C
scrutiny.
D A split-up
The DEH Company creates a new entity called KIP A company is trying to make it easier for investors to
D
Company out of one of its business lines. Shares in KIP are accurately value the company.
distributed to DEH shareholders based on their ownership
percentage in DEH. Which of the following is the best Which of the following is least likely to be a reason for a
description of this transaction? company to do a spin-off?
A A spin-off A A company becomes too large to manage.
B An equity carve-out B A company is profitable overall, but one area is struggling.
C A split-up C A company is trying to raise cash.
D A tracking stock D A company is trying to narrow its strategic focus.
Below are three possible benefits of a divestiture:
A company wants to keep control of a growing portion of Below are three possible benefits of a divestiture:
I the business while making it easier to value that portion of I A company wants to raise cash.
the business. II A company wants to avoid government intervention.
II A company wants to raise cash. III A company wants to be more focused.
A company wants to distribute an entire business area to Which of these is a company likely to accomplish with a split-
III
its existing shareholders. up?
A II and III only
Which of the following is most likely to be a reason for a B I, II, and III
company to do an equity carve-out? C III only
A A company is trying to narrow its strategic focus. D I and II only
A company is trying to provide stock in a new company to
B
its existing shareholders. Below are three possible benefits of a divestiture:
I A company wants to raise cash. Which of the following financial tools refers to a lender
A company wants to make it easier to value a portion of guaranteeing the acceptance of a payment request
II
the business. from an importer?
III A company wants to be more focused. A Letters of credit
Which of these is a company likely to accomplish with a B Time drafts
tracking stock?
C Bankers’ acceptance
A I, II, and III
B I and II only D Sight drafts
C II only
D I and III only Which of the following financial tools involves an
exporter sending goods to an importer before the good
Which of the following is a type of business divestiture? has been sold to a customer?
A Leveraged recapitalization A Letters of credit
B Equity carve-out B Countertrading
C Acquisition C Consignment
D Merger D Sight drafts
The HRS Company creates a new entity called KJT Which of the following factors does not affect the use
Company out of one of its business lines. HRS sells 30% of
the shares in KJT on the open market for cash. Which of the
of the discounted cash flow method on an international
following is the best description of this transaction? capital budgeting project compared to a domestic
A A spin-off capital budgeting project?
B An equity carve-out A Tax laws
C A tracking stock B Financial reporting requirements
D A split-up C Repatriation of earnings requirements
D Time value of money
Which of the following types of business divestitures would a
firm use in order to most effectively monitor the performance
of a strategic business unit?
A Spin-off Which of the following financial tools refers to bills for
B Equity carve-out imports payable upon receipt?
C Split-up A Letters of credit
D Tracking stock B Time drafts
In which of the following types of business divestitures does C Consignment
a firm sell a minority interest in the newly created firm? D Sight drafts
A Spin-off
B Equity carve-out Which of the following financial tools requires payment
C Split-up be made upon the completion of an obligated action?
D Tracking stock A Letters of credit
B Time drafts
Which of the following types of business divestitures takes C Consignment
place when a firm creates a new company based on one of D Sight drafts
its product lines?
A Spin-off
B Equity carve-out From the perspective of the exporter/seller, which of
C Split-up the following is the riskiest form of payment used in
D Tracking stock international trade?
A Open accounts
Which type of divestiture involves distributing a stock
B Letters of credit
dividend to a company’s current shareholders?
A A tracking stock C Time drafts
B A spin-off D Sight drafts
C An equity carve-out Which of the following is least likely to be a benefit of
D A split-up a company expanding internationally?
A Reducing legal and administrative expenses.
Which of the following types of business divestitures is often B Securing a new source of raw materials.
a result of government concern about monopolistic behavior? Being able to access a new source of employee
A Spin-off C
talent.
B Equity carve-out
D Easier access to new investors.
C Split-up
D Tracking stock
Which of the following describes countertrading?
A bank in Finland sends a notice to a seller in the
A United States guaranteeing that it will pay the seller
on the buyer’s behalf.
B A nonfinancial buyer in Cyprus creates a time draft
whose payment is guaranteed by a bank and then By choosing countertrade, it would become difficult
C
gives this draft to a seller in the United States as for Ted Co. secure new business in R-land.
payment for a purchase. By choosing countertrade, Ted Co. will be able to
D
A buyer in Mexico agrees to pay a seller in the keep the transaction costs low.
C
United States on a specified date.
A U.S. company sells a material to a South Korean
D
company in exchange for software. Which of the following is not normally used to finance
international transactions?
Which of the following describes cross-border A A banker’s acceptance
factoring? B A line of credit
A nonfinancial buyer in Israel creates a time draft C A foreign currency account
whose payment is guaranteed by a bank and then D Cross-border factoring
A
gives this draft to a seller in the United States as
payment for a purchase. Which of the following describes a letter of credit?
A seller in the United States ships goods to a buyer A factor in the United States contacts a factor in
in Switzerland and then the buyer in Switzerland A Germany to assist in the collection of accounts
B
signs an invoice acknowledging receipt of the receivable.
goods. A seller in the United States ships goods to a buyer
A factor in the United States contacts a factor in in the United Kingdom and then the buyer in the
C Greece to assist in the collection of accounts B
United Kingdom signs an invoice acknowledging
receivable. receipt of the goods.
A bank in Sweden sends a notice to a seller in the A buyer in Spain agrees to pay a seller in the United
D United States guaranteeing that it will pay the seller C
States immediately when goods are delivered.
on the buyer’s behalf. A bank in Canada sends a notice to a seller in the
D United States guaranteeing that it will pay the seller
Which of the following is least likely to be a benefit of on the buyer’s behalf.
a company expanding internationally?
Expanding to international markets increases the
A
market for a company’s products. Which of the following is least likely to be a benefit of
Expanding to international markets lowers a a company expanding internationally?
B
company’s cost of capital. Expanding to international markets gives a
Expanding to international markets increases the A
C company the opportunity to minimize its tax bill.
pool of talent from which a company can hire. Expanding to international markets increases the
Expanding to international markets increases a B chances that more investors will purchase the
D
company’s access to sources of capital. company’s stock.
Expanding to international markets simplifies a
All of the following relating to the advantages C
company’s supply chain.
associated with international diversification of a Expanding to international markets increases a
business are correct, except: D
company’s access to sources of capital.
International diversification allows access to scarce,
A
more competitive resources. Consider two countries: Country A and Country B. If
International diversification can lead to economies Country A's currency is more valuable than Country
B
of scale. B's, how will country A's imports from Country B be
International diversification helps in spreading affected?
C
business risks. A Imports will increase.
International diversification is preferred as it allows B Imports will decrease.
D the repatriation of profits very easily from other C Imports will not be affected.
countries to the domestic country. D Not enough information is given.
Ted Co. is a large organization that manufactures and
sells small industrial equipment. The company has its Makers, a footwear manufacturer, has decided to start
headquarters in T-land. Ted Co. has been contacted selling footwear in the international market. The firm
by a firm based out of R-land that desires to buy the has been contacted by Takers, a mid-sized shoe
equipment from Ted Co. in exchange for wheat retailer located in Country X to buy 1,000 pairs of
(countertrade). The currency of R-land is not freely shoes. Makers is keen on selling the footwear to
convertible. Takers. Since not much information is available
Which of the following statements is true regarding regarding Takers’ creditworthiness, Makers has
such a countertrade agreement? requested for a letter of credit.
The countertrade will increase the risk of foreign Which of the following statements is/are true regarding
A
exchange movements for Ted Co. such a letter of credit?
The importer of R-land may place an unrealistically I. Under the letter of credit, Takers would be the
B high value on the wheat it wishes to offer for beneficiary.
countertrade.
II. The letter of credit would provide Makers a Which of the following describes a banker’s
risk-free way of securing payment for the acceptance?
shoes. A nonfinancial buyer in Japan creates a time draft
III. Makers will be paid for the sale made once the whose payment is guaranteed by a bank and then
A
required shipping documents are submitted to gives this draft to a seller in the United States as
the transport company. payment for a purchase.
A I, II, and III A U.S. company sells a material to an Irish
B
B II and III only company in exchange for a different material.
C II only A seller in the United States sells a receivable
C
D III only payable in 200 days from a buyer in France.
A U.S. company sends goods to be sold in Japan to
A bank in France sends a notice to a seller in the D a Japanese company and the Japanese company
United States guaranteeing that it (the bank) will pay pays for the goods only when they are sold.
the seller on the buyer’s behalf. What is the correct
term to describe this arrangement? Which of the following describes consignment?
A A bankers’ acceptance A U.S. company sends goods to be sold in Italy to
B Cross-border factoring A an Italian company and the Italian company pays for
C A letter of credit the goods only when they are sold.
D Countertrading A buyer in Slovakia agrees to pay a seller in the
B United States immediately when goods are
A United States company sells software to a Japanese delivered.
company in exchange for marketing services in Japan. A buyer in Ukraine agrees to pay a seller in the
C
What is the correct term to describe this arrangement? United States for goods on a specified date.
A Countertrading A U.S. company sells software to a Japanese
B Cross-border factoring D company in exchange for a different type of
C A foreign currency account software.
D Forfaiting
Which of the following is least likely to be a benefit of
a company expanding internationally?
A nonfinancial buyer in Germany creates a time draft
Expanding to international markets makes it easier
whose payment is guaranteed by a bank and then A
to manage a company.
gives this draft to a seller in the United States as
payment for a purchase. What is the correct term to If a company’s domestic market is in recession,
B
describe this arrangement? growth in international markets may offset that.
A A sight draft Expanding to international markets increases the
B A letter of credit C opportunity for a company to obtain needed
resources.
C Forfaiting
Expanding to international markets increases the
D A bankers’ acceptance D
opportunity for a company to learn best practices.
Which of the following statements is true about
Which of the following describes forfaiting?
forfeiting?
A factor in the United States contacts a factor in
Forfeiting involves the purchase of foreign accounts
A Denmark to assist in the collection of accounts
A receivables by the forfeiter on a “without recourse”
receivable.
basis.
A seller in the United States sells a receivable
Forfeiting can be used for accounts receivables of B
B payable in 195 days from a buyer in Italy.
both domestic and international trades.
A buyer in Mexico agrees to pay a seller in the
Since the risk involved for the forfeiter is high,
C United States immediately when goods are
C forfeiting deals with short-term accounts receivables
delivered.
which fall due within 90 days.
A U.S. company sends goods to be sold in Brazil to
Forfeiting is available for small receivable accounts
D D a Brazilian company and the Brazilian company
and for all currencies.
pays for the goods only when they are sold.
Which of the following is least likely to be a challenge
Which of the following factors has the least influence
in evaluating international expansion projects?
on foreign currency exchange rates?
Forecasting the impact of foreign currency
A A Inflation rates
exchange rates on a project’s cash flows.
B Stock market activity
Choosing the correct tools to use to assess an
B C Interest rates
international project.
Forecasting the tax implications of an international D Ease of capital flow across borders
C
project.
State Bank of India has offered a spot rate quote on
Choosing the correct discount rate to use to assess
D Indian rupees (Rs.) of Rs. 42.47/$. The Indian rupee is
an international project.
quoted at a 30-day forward premium of 7.65% against
the dollar. What is the 30-day forward quote?
A Rs.39.2211/$
B Rs.45.7190/$ A $205.03
C Rs.42.1993/$ B $84.02
D Rs.42.7408/$ C €131.25
D €84.02
Which of the following factors has the least influence Which of the following statements concerning foreign
on foreign currency exchange rates? exchange rates is correct?
A Inflation rates A floating exchange rate system provides investors
B Current account deficits A the opportunity to profit from exchange rate
C The business cycle fluctuations.
D Income level A managed floating exchange rate system results in
B
stable exchange rates.
A fixed exchange rate system provides
C governments the ability to take actions to expand or
Starling Corp. purchased some components from a reduce their monetary supply.
Mexican manufacturer. It has to pay 110 million A floating exchange rate system reduces
Mexican pesos (MP) for the goods today. The D uncertainty for businesses working with foreign
exchange rate today is MP10.3540/$. What is the currencies.
dollar cost of this payable? (Round your final answer to
the nearest dollar.) Xecor Pharma just received revenues of A$2,372,300
A $110,000,000 in Australian dollars (A$). The only quotes
B $10,623,913 management received are A$2.0651/£ and $1.8538/£.
C $11,110,235 What is the U.S. dollar value of the company's
D $1,138,940,000 revenues? (Do not round your intermediate calculation.
Round your final answer to the nearest dollar.)
Bank of America quoted the 180-day forward rate on A $9,081,834
the Japanese Yen at $0.009702/¥. The spot rate was B $619,677
quoted at $0.009466/¥. What is the forward premium C $2,129,567
or discount on the Japanese Yen? (Round your final D $2,646,042
answer to the nearest percentage.)
A 2.5% premium The spot rate on the London market was
B 2.5% discount £0.5434/$, while the 90-day forward rate
C 5% premium was £0.5519/$. What is the annualized
D 5% discount forward premium or discount on the U.S.
dollar for the period? (Round your final
Given that the spot rate is ¥106.74/$ and the 180-day answer to one decimal place.)
forward quote is ¥100.37/$, we can say which of the A 1.6% premium
following? B 6.3% premium
The U.S. dollar is at a forward premium against the C 6.3% discount
A
Yen. D 1.6% discount
The Yen is at a forward discount against the U.S.
B
dollar.
The Yen is at a forward premium against the U.S. A company in Country A and a company
C
dollar. in Country B are both interested in
The U.S. dollar is at neither a premium nor a purchasing a product from a company in
D Country C that costs 1,000 units of
discount against the Yen.
Country C’s currency. The table below
Trident Corp. recently purchased machinery parts shows the amount of country C’s currency
worth 23.5 million Mexican Pesos (MP). Management that 1 unit of each country’s currency is
needs to find out the U.S. dollar cost of the payables. It worth at two different times. Based on this
has access to two quotes for Canadian dollars (C$): information, which statement is correct?
C$1.0774/$ and C$0.0981/MP. What will it cost Trident One Week
Today
in U.S. dollars to purchase 23.5 million Mexican Ago
pesos? One unit of 25 units of 28 units of
A $2,483,784 currency A currency C currency C
B $2,305,350 One unit of 31 units of 26 units of
C $2,139,735 currency B currency C currency C
D $25,318,900 The product is more expensive today
in Country A than one week ago
Venkat Ram purchased a pair of dress shoes in Italy A because Country A’s currency has
for €131.25. If the spot exchange rate is $1.5621/€, weakened relative to Country C’s
what is the equivalent cost of the shoes in American currency.
dollars? (Round your final answer to two decimal B The product is cheaper today in
places.) Country B than one week ago because
Country B’s currency has weakened C’s currency. The table below shows the
relative to Country C’s currency. amount of country C’s currency that 1 unit
The product is more expensive today of each country’s currency is worth at two
in Country B than one week ago different times. Based on this information,
C because Country B’s currency has which statement is correct?
weakened relative to Country C’s One Week
Today
currency. Ago
The product is cheaper today in One unit of 50 units of 45 units of
Country A than one week ago because currency A currency C currency C
D
Country A’s currency has weakened One unit of 44 units of 48 units of
relative to Country C’s currency. currency B currency C currency C
The product is cheaper today in
Zylex Corporation's German unit is looking Country B than one week ago because
A
to borrow €4.5 million from Deutsche Country B’s currency has strengthened
Bank. Deutsche Bank quotes a rate of relative to Country C’s currency.
three-month LIBOR plus 0.5% for the 90- The product is more expensive today
day loan. Currently, the three-month in Country B than one week ago
LIBOR is 4.175%. If the exchange rate on B because Country B’s currency has
the payoff date is €0.8334/$, what is strengthened relative to Country C’s
Zylex's interest cost in U.S. dollars? currency.
(Round your final answer to two decimal The product is more expensive today
places.) in Country A than one week ago
A $63,107.45 C because Country A’s currency has
B $252,429.81 strengthened relative to Country C’s
C $39,143.76 currency.
D $43,831.63 The product is cheaper today in
Country A than one week ago because
D
Country A’s currency has strengthened
The data below show the current relative to Country C’s currency.
exchange rates for countries X, Y, and Z
last year. The spot rate on the London market was £0.5434/$,
3.85 X pounds = $1 while the 90-day forward rate was £0.5519/$. What is
19.6 Y pesos = $1 the annualized forward premium or discount on the
44.6 Z crowns = $1 U.S. dollar for the period? (Round your final answer to
The data below show the current one decimal place.)
exchange rates for countries X, Y, and Z A 1.6% premium
this year. B 6.3% premium
4.20 X pounds = $1 C 6.3% discount
22.5 Y pesos = $1
D 1.6% discount
48.0 Z crowns = $1
Given these exchange rates, what
On September 22, Year 1, Yumi Corp., purchased
statement about the Y peso is true?
merchandise from an unaffiliated foreign company for
*Source: Retired ICMA CMA questions.
10,000 units of the foreign company's local currency.
It depreciated against the Z crown and
A On that date, the spot rate was $0.55. Yumi paid the
depreciated against the X pound.
bill in full on March 20, Year 2, when the spot rate was
It appreciated against the Z crown and $0.65. The spot rate was $0.70 on December 31, Year
B
appreciated against the X pound. 1. What amount should Yumi report as a foreign
It depreciated against the Z crown and currency transaction loss in its income statement for
C
appreciated against the X pound. the year ended December 31, Year 1?
It appreciated against the Z crown and A $1,500
D
depreciated against the X pound. B $0
C $500
D $1,000
Consider two countries: Country A and Country B. If
Country A's currency is more valuable than Country
B's, how will country A's imports from Country B be
affected?
A Imports will increase.
A company in Country A and a company B Imports will decrease.
in Country B are both interested in C Imports will not be affected.
purchasing a product from a company in D Not enough information is given.
Country C that costs 500 units of Country
Which of the following financial instruments is a C Purchase the Yen today on the spot market.
contract whereby organizations assume the foreign D Baljit does not need to purchase Yen.
exchange risk of another party? (Choice B) Correct. Since Baljit is risk averse, the company
A Currency future should not wait to purchase the Yen. The cost of the forward
B Currency swap contract is ¥278,450,000 ÷ ¥105.46/$ = $2,640,338 ÷ (1
+ .06 × 90 ÷ 360) = $2,601,318. The cost of purchasing the
C Currency option
Yen today is ¥278,450,000 ÷ (1 + .06 × 90 ÷ 360) =
D Currency insurance ¥274,334,975 ÷ ¥102.50/$ = $2,676,439.
Which of the following financial instruments is a Celio Inc. purchased equipment from a French firm
contract that fixes a currency exchange rate at a future and needs to pay €1,249,425 in 30 days. Celio is risk
date? averse. Celio has 3 choices on how to pay the
A Currency swap payable: (1) wait and purchase the Euros on the spot
B Currency option market on settlement date, (2) enter into a forward
C Currency insurance contract to purchase the Euros at the 30-day forward
D Currency future rate of $1.5512/€, or (3) or purchase the Euros today
on the spot market at a rate of $1.5708/€. The risk-free
Which of the following financial instruments is a rate is 5%. In France and in the U.S. What is the cost
contract that gives a firm the right but not the obligation today of the forward contract choice?
to engage in a foreign currency exchange? A $1,938,108
A Currency future B $1,930,066
B Currency swap C $1,244,241
C Currency option D $1,954,453
(Choice B) Correct. The cost today of the forward contract is
D Currency insurance
€1,249,425 × $1.5512/€ = $1,938,108 ÷ (1 + .05 ÷ 12) =
$1,930,066.
A US company needs to purchase a product from an
international customer for 5,000 euros to be paid 30
days from the purchase date. On the purchase date,
the exchange rate is $1.25 per 1 euro. The company
expects the exchange rate to be between $1.24 and
$1.27 per 1 euro in 30 days. Based on this, which of
the following actions should the company take to best
manage its currency risk?
Enter into a currency futures contract to buy euros
A
for $1.26 in 30 days.
Enter into a currency futures contract to sell euros
B
for $1.27 in 30 days.
C Enter into a currency swap contract.
D Do nothing.
The company “locks in” an exchange rate of $1.26 per euro
with this contract. This provides cash flow certainty.
However, if the spot rate is below $1.26 in 30 days (for
example, $1.24 or $1.25) it will not be able to buy at the
lower rate under this contract. It will trade certainty for the
ability to benefit from a lower exchange rate with this
contract.
Palermo, Corp. sold equipment to a French firm.
Palermo will be paid €4,275,000 in 90 days. The bank
has given the firm a 90-day forward quote of $1.5487/€
Baljit Inc. purchased machinery from a Japanese firm to purchase Euros forward, and $1.5922/€ to sell
and will have to pay ¥278,450,000 in 90 days. Baljit Euros forward. Palermo decided to wait 90 days to sell
has three choices: (1) wait 90 days and purchase the the Euros, when the spot rate was $1.5645/€. How
Yen on the spot market on settlement date, (2) enter much additional dollar revenue did Palermo gain or
into a forward contract with a rate of ¥105.46/$ to buy lose by waiting to sell the Euros on the spot market
the required Yen on the settlement date, or (3) instead of selling forward the Euros? (Round your final
purchase the Yen today on the spot market at a rate of answer to the nearest dollar.)
¥102.50/$. The risk-free rate is 6% in both Japan and A $118,417 gain
the US. Assuming Baljit is risk averse, what is its best B $118,417 loss
option? C $67,545 gain
Wait and purchase the Yen on the spot market on D $67,545 loss
A
settlement date. Selling the Euros on the spot market yielded Palermo
B Enter into the forward contract to purchase the Yen. €4,275,000 × $1.5645 = $6,688,238. Had Palermo used the
forward contract, the Euros would have yielded €4,275,000 ×
$1.5922 = $6,806,655, a loss of $118,417. Which of the following statements is correct?
A currency swap is a contract where two companies
Celio Inc. purchased equipment from a French firm A
exchange (swap) different currencies.
and needs to pay €1,249,425 in 30 days. Celio is risk A currency futures contract gives the buyer the
averse. Celio has 3 choices on how to pay the B right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell foreign
payable: (1) wait and purchase the Euros on the spot currency at a pre-determined price.
market on settlement date, (2) enter into a forward
A currency options contract obligates the buyer to
contract to purchase the Euros at the 30-day forward
C buy or sell foreign currency at a pre-determined
rate of $1.5512/€, or (3) or purchase the Euros today
price.
on the spot market at a rate of $1.5708/€. The risk-free
rate is 5%. In France and in the U.S. What is Celio's Speculators simultaneously purchase foreign
best option? D currency in one market and sell it in another market
Wait and purchase the Euros on the spot market in at a slightly higher price.
A
30 days.
B Enter into the forward contract.
Celio Inc. purchased equipment from a French firm
C Purchase the Euros on the spot market today.
and needs to pay €1,249,425 in 30 days. Celio is risk
D Celio does not need to purchase Euros. averse. Celio has 3 choices on how to pay the
(Choice B) Correct. The cost today of the forward contract is
payable: (1) wait and purchase the Euros on the spot
€1,249,425 × $1.5512/€ = $1,938,108 ÷ (1 + .05 ÷ 12) =
$1,930,066. The cost today of purchasing the Euros in the market on settlement date, (2) enter into a forward
spot market €1,249,425 ÷ (1 + .05 ÷ 12) = €1,244,241 contract to purchase the Euros at the 30-day forward
needed today × spot rate $1.5708/€ = $1,954,453. The rate of $1.5512/€, or (3) or purchase the Euros today
company should not wait and purchase the Euros because it on the spot market at a rate of $1.5708/€. The risk-free
is risk averse. rate is 5%. In France and in the US. What is the cost
today of purchasing the Euros today on the spot
market?
A U.S. company has accounts receivable from a Swiss A $1,938,108
company for 100,000 Swiss francs (CHF) due in three B $1,930,066
months. At the time of contract, the exchange rate was C $1,244,241
1.0 CHF =1.0 USD. The U.S. company wishes to D $1,954,453
manage its foreign exchange exposure and therefore (Choice D) Correct. The cost today of purchasing the Euros
*Source: Retired ICMA CMA Exam Questions. in the spot market €1,249,425 ÷ (1 + .05 ÷ 12) = €1,244,241
A buys a currency swap. needed today × spot rate $1.5708/€ = $1,954,453.
B buys U.S. dollar futures.
C sells U.S. dollar futures.
D sells a Swiss francs interest rate swap. Baljit Inc. purchased machinery from a Japanese firm
and will have to pay ¥278,450,000 in 90 days. Baljit
(Choice B) The risk to the U.S. company is that if the dollar has three choices: (1) wait 90 days and purchase the
strengthens against the Swiss franc during the next three Yen on the spot market on settlement date, (2) enter
months, the amount effectively received will decrease. The into a forward contract with a rate of ¥105.46/$ to buy
U.S. company needs to own a financial instrument that will the required Yen on the settlement date, or (3)
increase in value if the dollar strengthens against the Swiss purchase the Yen today on the spot market at a rate of
franc. That way, the gain from the new instrument will offset ¥102.50/$. The risk-free rate is 6% in both Japan and
the loss on the accounts receivable. U.S. dollar futures will
the US. What is the cost today to Baljit of the forward
increase in value if the dollar strengthens as this instrument
gets its value based on the value of the dollar. contract choice?
A $2,640,338
A US company sells a product to an international B $2,601,318
customer for 5,000 euros to be paid 30 days from the C $274,334,975
sale date. On the sale date, the exchange rate is $1.20 D $2,676,439
per 1 euro. The company expects the exchange rate to (Choice B) Correct. The cost of the forward contract is
be between $1.22 and $1.24 per 1 euro in 30 days. ¥278,450,000 ÷ ¥105.46/$ = $2,640,338 ÷ (1 + .06 × 90 ÷
Based on this, which of the following actions should 360) = $2,601,318.
the company take to best manage its currency risk?
Enter into a currency futures contract to sell euros
A A US company sells a product to an international
for $1.22 in 30 days.
Enter into a currency options contract to buy euros customer for 1,000 euros to be paid 30 days from the
B sale date. On the sale date, the exchange rate is $1.25
for $1.22 in 30 days.
per 1 euro. The company enters a currency futures
C Do nothing.
contract to sell 1 euro for $1.26 on the payment date.
Enter into a currency options contract to sell euros
D On the payment date, the exchange rate is $1.31 per 1
for $1.22 in 30 days. euro. How much will the US company receive on the
The company “locks in” an exchange rate of $1.22 per euro
payment date?
with this options contract even if the exchange rate is less
than $1.22 per euro. However, it can choose not to sell if the A $1,250.00
exchange rate is more than $1.22 per euro with this contract. B $1,260.00
C $1,310.00
D $793.65 next year, purchasing power parity would predict that
(Choice B) Correct. Companies can use currency futures the exchange rate next year should be closest to
contracts to manage exchange rate risk. With a currency *Source: Retired ICMA CMA questions.
futures contract, the buyer must buy or sell foreign currency A 1 Turkish lira = 10.8 Indian rupees.
at a pre-determined price. It does not have the option to not
B 1 Turkish lira = 12.9 Indian rupees.
buy or sell if exchange rates change in a way that benefits
them not to sell according to the contract. In this example, C 1 Turkish lira = 13.3 Indian rupees.
the US company would “prefer” to sell the 1,000 euros at the D 1 Turkish lira = 14.4 Indian rupees.
spot rate of $1.31 per euro. However, it cannot do that as it is
obligated to sell under the futures contract for $1.26 per At equilibrium, a good that cost 1 lira in Turkey will cost 12
euro. Therefore, it will receive $1,260.00 on the payment rupees in India. If inflation is 20% in Turkey, the good will
date (1,000 euros × $1.26 per euro). now cost 1.2 lira (1 × 1.20) because of the 20% inflation.
That same good will cost 12.96 rupees in India because of
the 8% inflation (12 × 1.08). To maintain parity, the exchange
Baljit Inc. purchased machinery from a Japanese firm rate will change to 1 lira being equal to 10.8 rupees (12.96 /
and will have to pay ¥278,450,000 in 90 days. Baljit 1.2).
has three choices: (1) wait 90 days and purchase the
Yen on the spot market on settlement date, (2) enter
into a forward contract with a rate of ¥105.46/$ to buy Kapona Industries has purchased equipment from a
the required Yen on the settlement date, or (3) Korean firm for a total cost of 11,500,000 Korean won.
purchase the Yen today on the spot market at a rate of The firm has to pay in 90 days. J. P. Morgan has given
¥102.50/$. The risk-free rate is 6% in both Japan and the firm a 90-day forward quote of $0.0009791/won to
the US. What is the cost today if Baljit purchases the purchase Korean won forward, and $0.001022/won to
Yen today on the spot market? sell Korean won forward. Kapona decided to wait and
A $2,640,338 purchase the Korean won on the spot market on
B $2,601,318 settlement date. On the day the payment is due,
Kapona purchases the Korean won on the spot market
C $274,334,975
at a rate of $0.001004/ won. How much would Kapona
D $2,676,439 have saved or lost by hedging with a forward contract?
(Choice D) Correct. The cost of purchasing the Yen today is (Round your final answer to the nearest dollar.)
¥278,450,000 ÷ (1 + .06 × 90 ÷ 360) = ¥274,334,975 ÷
¥102.50/$ = $2,676,439. A $207 loss
B $207 savings
C $286 loss
Which of the following is not a financial instrument D $286 savings
used to reduce risk exposure associated with foreign
currency exchange rates? (Choice D) Correct. Purchasing the Korean won on the spot
A Currency future market cost Kapona 11,500,000 × 0.001004 = $11,546. Had
B Currency swap Kapona used the forward contract, the Korean won would
have cost 11,500,000 × 0.0009791 = $11,260, a savings of
C Currency stock $286
D Currency option
Carrington Industries sold equipment to a Mexican
A US company sells a product to an international firm. Carrington will be paid 41,275,000 pesos in 30
customer for 4,000 euros to be paid 30 days from the days. The bank has given the firm a 30-day forward
sale date. On the sale date, the exchange rate is $1.18 quote of $0.09739/peso to purchase Mexican pesos
per 1 euro. The company enters a currency options forward, and $0.09322/peso to sell Mexican pesos
contract to sell 1 euro for $1.22 on the payment date. forward. Carrington decided to wait 30 days to sell the
On the payment date, the exchange rate is $1.25 per 1 pesos, when the spot rate was $0.09596/peso. How
euro. How much will the US company receive on the much additional dollar revenue did Carrington gain or
payment date? lose by waiting to sell the pesos on the spot market
A $4,720.00 instead of selling forward the pesos? (Round your final
B $4,880.00 answer to the nearest dollar.)
A $113,093 gain
C $5,000.00
B $113,093 loss
D $3,200.00
In this example, the US company would rather sell the 4,000 C $59,023 gain
euros at the spot rate of $1.25 per euro rather than under the D $59,023 loss
options contract for $1.22 per euro. Therefore, it will receive (Choice A) Correct. Selling the Mexican pesos on the spot
$5,000.00 on the payment date (4,000 euros × $1.25 per market yielded Carrington MP 41,275,000 × $0.09596 =
euro). $3,960,749. Had Carrington used the forward contract, the
Mexican pesos would have yielded MP 41,275,000 ×
$0.09322 = $3,847,656, a gain of $113,093.
The exchange rate between the Turkish lira and the
Indian rupee is currently 1 Turkish lira equals 12 Indian
rupees. Assuming the inflation rate in Turkey will be A Canadian company has Mexican suppliers and
20% next year, and in India the inflation rate will be 8% Mexican customers. Trade credit is used in both cases.
Sales to Mexican customers are approximately two
times the purchases from Mexican suppliers. The
Canadian company could eliminate its transaction
exposure with the Mexican suppliers and Mexican
customers with which one of the following policies?
Denominate all accounts payable in Mexican pesos
A and denominate all accounts receivable in
Canadian dollars.
Denominate all accounts payable in Mexican pesos
B and denominate all accounts receivable in Mexican
pesos.
Denominate all accounts payable in Canadian
C dollars and denominate all accounts receivable in
Canadian dollars.
Denominate all accounts payable in Canadian
D dollars and denominate all accounts receivable in
Mexican pesos.
Tamcon Industries has purchased equipment from a
Brazilian firm for a total cost of 1,272,500 Brazilian
reals (BR). The firm has to pay in 30 days. Citicorp has
given the firm a 30-day forward quote of $0.6123/BR to
purchase Brazilian reals forward, and a quote of
$0.6421 to sell Brazilian reals forward. Tamcon
decided to wait and purchase the Brazilian reals on the
spot market on settlement date. On the day the
payment is due, Tamcon purchases the Brazilian reals
at the spot rate of $0.6317/BR. How much would
Tamcon have saved or lost by hedging with a forward
contract? (Round your final answer to the nearest
dollar.)
A $24,686 savings
B $24,686 loss
C $13,234 savings
D $13,234 loss
(Choice A) Correct. Purchasing the Brazilian reals on the
spot market cost Tamcon BR 1,272,500 × 0.6317 =
$803,838. Had Tamcon used the forward contract the
Brazilian reals would have cost BR 1,272,500 × 0.6123 =
$779,152, a savings of $24,686.
You might also like
- Responsibility Transfer Pricing Test Bank Financial Management AccountingNo ratings yetResponsibility Transfer Pricing Test Bank Financial Management Accounting41 pages
- ManAcc A Problem Set Incremental AnalysisNo ratings yetManAcc A Problem Set Incremental Analysis6 pages
- Shareholder'S Equity Multiple Choice Questions50% (2)Shareholder'S Equity Multiple Choice Questions7 pages
- 1 5 Mas - Lecture Notes Armin Glenn Araneta, Cpa EconomicsNo ratings yet1 5 Mas - Lecture Notes Armin Glenn Araneta, Cpa Economics5 pages
- Cost Concepts, Classification and Segregation: M.S.M.CNo ratings yetCost Concepts, Classification and Segregation: M.S.M.C7 pages
- Capital Structure and Leverage: Multiple Choice: ConceptualNo ratings yetCapital Structure and Leverage: Multiple Choice: Conceptual53 pages
- FEU SILANG Leverage and Capital Structure OCTOBER 2019No ratings yetFEU SILANG Leverage and Capital Structure OCTOBER 201911 pages
- Additional Funds Needed - Exercises - QuestionsNo ratings yetAdditional Funds Needed - Exercises - Questions4 pages
- Dividend Policy and Retained Earnings Guide100% (2)Dividend Policy and Retained Earnings Guide3 pages
- ICAREO First Preboard Examination FARAP Batch 9No ratings yetICAREO First Preboard Examination FARAP Batch 916 pages
- AT Quizzer 13 - Reporting Issues (2TAY1718) PDF0% (1)AT Quizzer 13 - Reporting Issues (2TAY1718) PDF10 pages
- Part 2 Corp Finance II (Stocks & Bonds) - Sol 14 Jul 2024No ratings yetPart 2 Corp Finance II (Stocks & Bonds) - Sol 14 Jul 202444 pages
- Business Combinations and Takeover Strategies100% (1)Business Combinations and Takeover Strategies3 pages
- Proposal - Gaming Company - DPL - Rishabh NareshNo ratings yetProposal - Gaming Company - DPL - Rishabh Naresh6 pages
- Admission To Professional Degree Courses in Nursing and Paramedical Streams-2021No ratings yetAdmission To Professional Degree Courses in Nursing and Paramedical Streams-20219 pages
- Empowering India's Vulnerable CommunitiesNo ratings yetEmpowering India's Vulnerable Communities5 pages
- SignedOfferLetter 01-16-25 52935 PM ButterballNo ratings yetSignedOfferLetter 01-16-25 52935 PM Butterball2 pages
- Retention of Elearning Development Manager (Ilt Manager)No ratings yetRetention of Elearning Development Manager (Ilt Manager)5 pages
- Summer Internship Report-Liquid Fund AnalysisNo ratings yetSummer Internship Report-Liquid Fund Analysis63 pages
- Return On Invested Capital and Profitability Analysis: Semester 1 2020/2021 Art, PatNo ratings yetReturn On Invested Capital and Profitability Analysis: Semester 1 2020/2021 Art, Pat21 pages
- Delta Air Lines, GBD Inc. Organizational Analysis100% (2)Delta Air Lines, GBD Inc. Organizational Analysis29 pages
- Case Study Greener Environmental ServicesNo ratings yetCase Study Greener Environmental Services2 pages
- Logistics & Technology: MOUPIA SAHA - 191051014No ratings yetLogistics & Technology: MOUPIA SAHA - 19105101410 pages
- Aplab EGM Notice: Share Capital ChangesNo ratings yetAplab EGM Notice: Share Capital Changes23 pages
- Types and Roles of Entrepreneurship: The Value of Different Types of Entrepreneurs For The Dutch Economy and SocietyNo ratings yetTypes and Roles of Entrepreneurship: The Value of Different Types of Entrepreneurs For The Dutch Economy and Society118 pages
- CH 06 - Intercompany Transfers of Services and Noncurrent Assets - Key Answer100% (1)CH 06 - Intercompany Transfers of Services and Noncurrent Assets - Key Answer41 pages