Title: Introduction to RC
Circuits
Objective:
To understand the basic principles of RC circuits and analyze
their behavior in different scenarios.
Introduction:
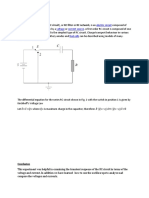
RC circuits are electrical circuits that consist of a resistor (R)
and a capacitor (C) connected in series or parallel. They are
fundamental in electronics and are widely used in
applications like filters, timers, and oscillators.
Theory:
1. Resistor (R): Limits the flow of current in the circuit.
2. Capacitor (C): Stores and releases electrical energy. Its
behavior is governed by the equation: where is the
charge, is the capacitance, and is the voltage.
3. RC Time Constant (): The time constant is given by: It
determines how quickly the capacitor charges or
discharges.
Applications:
1. Low-Pass Filters: Allow low-frequency signals to pass
while blocking high-frequency signals.
� 2. High-Pass Filters: Allow high-frequency signals to pass
while blocking low-frequency signals.
3. Timers: Used in circuits to delay signals or create time
intervals.
Practical Example:
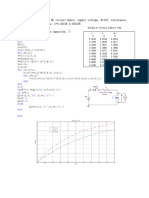
Consider an RC circuit with a 1 k resistor and a 1 capacitor
connected in series. When a 5V supply is applied:
1. The time constant is:
2. The capacitor charges to 63% of the supply voltage
within one time constant.
Conclusion:
RC circuits are essential building blocks in electronics.
Understanding their behavior helps in designing circuits for
various applications like signal processing and timing.