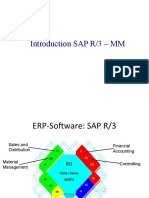
SAP and ERP
SAP and ERP stands for:
• ERP - Enterprise Resource Planning
• SAP - Systems Applications and Products
• SAP system consists of a number of fully integrated modules, which covers
virtually every aspect of business management.
SAP as an ERP
• No duplication, discontinuity, and redundancy in data
• Provides information across departments in real time.
• Provides control over various business processes
• Increases productivity, better inventory management, promotes quality, effective
human resources management, reduced overheads, boosts profits
• Increased throughput and improved customer services
SAP R/3
R/3 - Real-time data processing, 3-tier/layer
1. Database
2. Application
3. Presentation/client (SAPgui)
SAP Modules
Materials Management (MM)
Sales & Distribution (SD)
Warehouse Management (WM)
Finance and Controlling (FICO)
Production Planning(PP)
Quality Management (QM)
Transportation Management (TM)
Logistics and Execution (LE)
Human Capital Management (HCM)
BASIS (Technical Module)
ABAP (Technical Module)
Page # 1
� Materials Management
MM is a process for planning, organizing and controlling all the activities involved in the
flow of materials and services into an organization.
A business function for planning, purchasing, moving and storing materials
Organisational Structure in SAP MM
Client
Company Code Company Code
Plant Plant Plant
Storage Storage Storage Storage
Location Location Location Location
Master Data in SAP MM
• Master data comprises data records that are stored in the database for a long period
of time in a centralized location
• Used and processed on a cross-application and cross functional/dept. basis
• Avoid multiple storage and redundancy of data
• Reduce human effort and errors
• Automatic copy of data to documents
Page # 2
�1. Material Master
2. Vendor Master
3. Purchase Info Record
4. Source List
5. Bill of Material (BOM)
Material Master
• Central source of material – specific data
• Integration of all material data in a single database
• All the below areas can jointly access the stored data:
• Materials Planning — for material requirements planning
• Inventory management — for posting goods movements and physical inventory
management
• Accounting — for material valuation
• Purchasing — for ordering purposes
Vendor Master
• information about the vendors of a company, names of important contacts, address
• Mode of communication
• Terms of payment
• Currency used for transactions with the vendor
Purchase info Master data
• The availability period during which the vendor can supply the material
• Quotation and ordering data; last PO#
• Planned delivery time (lead time to deliver the material)
• Vendor evaluation data
• Tolerance limits for over/under deliveries
• Prices and conditions for the relevant purchasing organization or plant
Source List
• The source list answers question: "Which vendors can supply a material at a given
point of time?”
• Supplementing source determination with a quota arrangement
• Defining a source as a fixed source
• Blocking a source
• Defining a source in a planning run
Page # 3
�Bill of Material (BOM)
• A bill of material (BOM) is a complete, formally structured list of components that
make up a product or an assembly.
• The list contains a description for each component, together with quantity and unit of
measure.
• BOM is used to determine the material requirements in the subcontracting process
and the planning run (Material Requirements Planning )
Transaction codes:
Material Master: Create – MM01 Edit – MM02 Display – MM03
Vendor Master: Create – XK01 Edit – XK02 Display – XK03
Purchase Info Record: Create – ME11 Edit – ME12 Display – ME13
Source List: Create – ME01 Edit – ME01 Display – ME03
Bill of Material (BOM): Create – CS01 Edit – CS02 Display – CS03
Profit center of an organization is to route all profitability and balance sheet related
information to a profit center. Company code is a profit center.
Storage location is the sub-division of plant where the stocks are physically stored and
maintained within a plant. It is a must to maintain least one storage location for one plant
Plant can be operational unit or manufacturing unit or a sales branch of an organization.
In MM, plant can be defined as a location that holds valuated Inventory.
Purchasing group is a unit of purchasing organization responsible for day to day buying
activities and control procurement activity.
Purchasing organization is an entity of MM responsible to procure materials or services
with negotiation terms and conditions from vendors or internal plant.
Page # 4
�Procurement to Pay process (P2P)
1. ME51N - Create Purchase Requisition
2. ME21N - Create Purchase Order
3. MIGO - Goods Receipt (GR)
4. MIRO - Invoice Verification
5. MRBR - Invoice Release
6. F-53 - Payment to Vendor
T-codes of reports in MM
1. ME5A – List of Purchase Requisitions
2. ME2N - List of Purchase Orders
3. MB51 – List of Material documents
4. MIR5 – List of Invoice documents
5. MMBE – Stock Overview
6. MB52 – Stock Overview multiple materials
Procurement – Return Process
1. MIGO - Goods Return
2. MIRO - Credit Memo
3. MRBR - Invoice Release
4. F-52 - Incoming Payment
Reports in MM
ME5A – List of Purchase Requisitions
ME2N - List of Purchase Orders
MB51 – List of Material documents
MIR5 – List of Invoice documents
MMBE – Stock Overview
MB52 – Stock Overview multiple materials
Page # 5
� Warehouse Management
A storage type is a storage space, storage facility, or storage zone, defined for a
warehouse number in Extended Warehouse Management (EWM). The storage type is a
physical or logical subdivision of a warehouse complex. A storage type consists of one or
more storage bins.
Commonly-used physical storage types in EWM are:
• Bulk storage area
• General storage area
• High rack storage area
• Fixed bin storage area
• Rack storage area
A storage section is an organizational subdivision of a storage type that groups
together storage bins with similar features for the purpose of putting away stock. The
criteria for grouping bins for example: heavy parts, bulky materials, fast-moving items,
slow-moving items.
Page # 6
�Storage bins are storage spaces or slots in Warehouse Management (WM). The storage
bin is the smallest available unit of space in a warehouse where the goods are or can be
stored.
Quant is the details of the goods stored (content) in a bin. It provides unit of measure,
volume, size and additional information like – number of pieces, weight, pallets etc. of the
stored goods.
Quant number is a temporary unique identification number (a digital code) system assigns
to a bin when goods are placed in a bin.
System will delete the quant number when the goods are moved/cleared from the bin.
Putaway Process
LT04 - Create Transfer Order from Transfer Request (Putaway)
LT12 - Confirmation of Transfer Order
Bin to Bin Transfer
LT01 - Create Transfer Order
LT12 - Confirmation of Transfer Order
Pre-requisite for Bin to Bin transfer
LX01 – List of empty bins
LS24 – stock by storage type by bin
Return Process
LT06 - Create Transfer Order from Transfer Request (Return)
LT12 - Confirmation of Transfer Order
T-Codes for Reports in WM
LB10 – List of Transfer Requests
LT22 – List of Transfer Orders
Page # 7
� Sales & Distribution
Master data:
1. Material Master
2. Customer Master
3. Customer Material Info Record
Sales organization designs the company as per the sales requirements and responsible for
sales and distribution of goods and services. The selling unit is represented as a legal unit.
Sales Organisational structure
Distribution Channel is the process of distributing the goods or services to the
customers. It is selection criteria for grouping customers. One or more distribution
channel can serve the same customer.
A division is a way to group similar products or product lines in SAP. When you create a
material master record in SAP, you create it for a particular division. A division is also one
of the rules used to determine the sales area.
Sales Area is simply a combination of Sales Organization, Distribution Channel and
Division. It defines strategy of market reach, i.e. a Distribution Channel to sale a good or
service belonging to a particular division
Page # 8
�Sales Process steps
1. VA11 - Create Inquiry
2. VA21 - Create Quotation
3. VA41 - Create Contract
4. VA01 - Create Sales Order
5. VL01N - Create Delivery
6. LT03 - Create Transfer Order/Picking
7. LT12 - Confirmation of Transfer Order
8. VL02N - Post Goods Issue
9. VF01 - Create Billing Document
10. F-28 - Receipt of Payment
Sales return steps:
1. VA01 - Return Sales Order
2. VL01N - Return Delivery
3. VL02N - Post Goods Receipt
4. VF01 - Create Credit Memo
5. F-31 - Out going payment
Reports
VA15 – List of Inquiries
VA25 – List of Quotations
VA45 – List of Contracts
VA05 – List of sales orders
VL06F – List of Outbound deliveries
VF05 – List of Billing documents
Page # 9