0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views30 pagesAPP Assignment
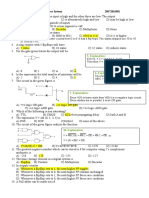
The document contains a series of Java and Python programming examples demonstrating various concepts such as control structures, functions, classes, inheritance, polymorphism, database connectivity, GUI design, threading, and socket programming. Each example includes code snippets that illustrate how to implement specific functionalities, such as calculating sums, generating pay slips, and creating simple calculators. Additionally, there are examples of constructing finite automata and performing algebraic manipulations using symbolic computation.
Uploaded by
undestinedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views30 pagesAPP Assignment
The document contains a series of Java and Python programming examples demonstrating various concepts such as control structures, functions, classes, inheritance, polymorphism, database connectivity, GUI design, threading, and socket programming. Each example includes code snippets that illustrate how to implement specific functionalities, such as calculating sums, generating pay slips, and creating simple calculators. Additionally, there are examples of constructing finite automata and performing algebraic manipulations using symbolic computation.
Uploaded by
undestinedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 30