0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views20 pagesWww-Vedantu-Com-Re
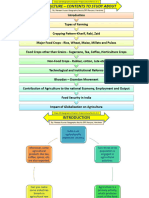
The document provides comprehensive notes on Chapter 4 Agriculture from Class 10 CBSE Geography, covering types of farming, major crops, cropping patterns, and the economic significance of agriculture in India. It highlights the contribution of agriculture to employment and the national economy, as well as the impact of technological reforms and globalization. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of revision notes for effective study and understanding of agricultural concepts.
Uploaded by
wetis26694Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views20 pagesWww-Vedantu-Com-Re
The document provides comprehensive notes on Chapter 4 Agriculture from Class 10 CBSE Geography, covering types of farming, major crops, cropping patterns, and the economic significance of agriculture in India. It highlights the contribution of agriculture to employment and the national economy, as well as the impact of technological reforms and globalization. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of revision notes for effective study and understanding of agricultural concepts.
Uploaded by
wetis26694Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20