0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views37 pages02-fMRIDA Slides
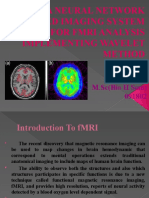
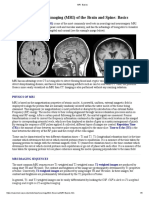
The document outlines a course on fMRI data analysis, focusing on data manipulation and plotting using Python. It discusses the differences between structural and functional neuroimaging, including spatial and temporal resolution, and introduces the structure of MRI and fMRI data. Additionally, it covers data formats such as DICOM and NIfTI, and provides links to Python exercises and homework assignments related to the course.
Uploaded by
Joao DuqueCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views37 pages02-fMRIDA Slides
The document outlines a course on fMRI data analysis, focusing on data manipulation and plotting using Python. It discusses the differences between structural and functional neuroimaging, including spatial and temporal resolution, and introduces the structure of MRI and fMRI data. Additionally, it covers data formats such as DICOM and NIfTI, and provides links to Python exercises and homework assignments related to the course.
Uploaded by
Joao DuqueCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 37