0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views3 pagesClass7 CBSE Science Light Module
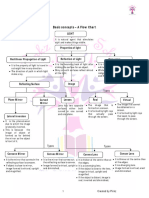
The document is a complete module on light for Class 7 CBSE Science, covering topics such as the nature of light, reflection, refraction, mirrors, lenses, and the human eye. It includes explanations of laws of reflection, types of mirrors and lenses, image formation, and applications of light, along with multiple choice and short answer questions for assessment. The module serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental concepts of optics.
Uploaded by
afrinshabbir82Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views3 pagesClass7 CBSE Science Light Module
The document is a complete module on light for Class 7 CBSE Science, covering topics such as the nature of light, reflection, refraction, mirrors, lenses, and the human eye. It includes explanations of laws of reflection, types of mirrors and lenses, image formation, and applications of light, along with multiple choice and short answer questions for assessment. The module serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental concepts of optics.
Uploaded by
afrinshabbir82Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3