0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesDatabase Files
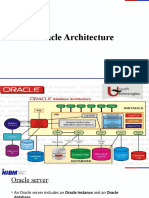
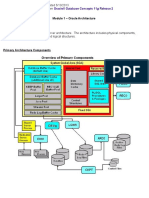
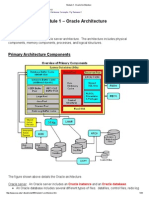
The document outlines the components of a database, including datafiles, control files, and redo log files, emphasizing their importance for data integrity and recovery. It also describes backup files, parameter files, password files, alert logs, and trace files, detailing their functions and significance in database management. Losing any of these critical files can result in the loss of the database or hinder recovery efforts.
Uploaded by
Katelyn RamphalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesDatabase Files
The document outlines the components of a database, including datafiles, control files, and redo log files, emphasizing their importance for data integrity and recovery. It also describes backup files, parameter files, password files, alert logs, and trace files, detailing their functions and significance in database management. Losing any of these critical files can result in the loss of the database or hinder recovery efforts.
Uploaded by
Katelyn RamphalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4