0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views2 pagesComputer Science Notes For Class IV
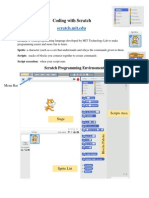
The document provides an overview of Scratch 3.0, a visual programming language developed by MIT for teaching coding through creative projects. It details the components of the Scratch interface, including the stage, sprites, backdrops, and various programming blocks used for motion, appearance, sound, and control. Additionally, it explains how to work with sprites, customize backdrops, and utilize input and looping blocks in projects.
Uploaded by
jagriti dudejaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views2 pagesComputer Science Notes For Class IV
The document provides an overview of Scratch 3.0, a visual programming language developed by MIT for teaching coding through creative projects. It details the components of the Scratch interface, including the stage, sprites, backdrops, and various programming blocks used for motion, appearance, sound, and control. Additionally, it explains how to work with sprites, customize backdrops, and utilize input and looping blocks in projects.
Uploaded by
jagriti dudejaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2