0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesLecture Slides 08 082-Processes-Creating
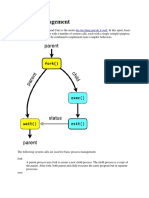
The document discusses processes in computing, specifically focusing on the fork-exec model used to create new processes. It explains how the fork() system call generates a child process that is a copy of the parent process, and the execve() system call replaces the child's code with a different program. Additionally, it highlights the differences in process creation between Linux and Windows, along with other relevant system calls for process management.
Uploaded by
yihuangeceCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesLecture Slides 08 082-Processes-Creating
The document discusses processes in computing, specifically focusing on the fork-exec model used to create new processes. It explains how the fork() system call generates a child process that is a copy of the parent process, and the execve() system call replaces the child's code with a different program. Additionally, it highlights the differences in process creation between Linux and Windows, along with other relevant system calls for process management.
Uploaded by
yihuangeceCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5