Procedures & Functions
IGCSE Computer Science - 0478
CS 0478
� • Functions and procedures are a type of sub
program, a sequence of instructions that perform a specific
task or set of tasks
• Procedures and functions are defined at the start of the code
• Sub programs are often used to simplify a program by breaking
it into smaller, more manageable parts
CS 0478
�• Parameters are values that are passed into a sub program.
• Parameters can be variables or values and they are located in br ackets after the
name of the sub program
• Example:
FUNCTION TaxCalculator(pay,taxcode) RETURNS DataType
PROCEDURE TaxCalculator(pay,taxcode)
CS 0478
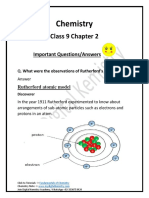
� What's the difference between a function and
procedure?
A Function returns a value whereas a procedure does
not
CS 0478
� Procedures Definition
Procedures are defined using the PROCEDURE keyword in pseudocode
A procedure can be written as:
PROCEDURE <identifier> To call a procedure, it can be written as:
<statements>
ENDPROCEDURE CALL <identifier>
CALL <identifier>(Value1,Value2...)
Or if parameters are being used:
PROCEDURE <identifier>(<par1>:<data type>, <par2>:<data type>)
<statements>
ENDPROCEDURE
CS 0478
� Function Definition
Functions
Functions are defined using the FUNCTION keyword in pseudocode or def keyword in
Python
Functions always return a value so they do not use the CALL function, instead they are
called within an expression
A function can be written as:
FUNCTION <identifier> RETURNS <data type>
<statements>
ENDFUNCTION
FUNCTION <identifier>(<par1>:<datatype>, <par2>:<datatype>) RETURNS <data type>
<statements>
ENDFUNCTION
CS 0478
� Function Calling
To call a function, it can be written as:
Identifier FunctionName( )
Identifier FunctionName(par1,par2)
OR
OUTPUT FunctionName( )
OUTPUT FunctionName(par1,par2 )
CS 0478
� Types of Variables
Local Variables
What is a local variable?
• A local variable is a variable declared within a specific scope, such
as a function or a code block
• Local variables are accessible only within the block in which they
are defined, and their lifetime is limited to that particular block
• Once the execution of the block ends, the local variable is
destroyed, and its memory is released
CS 0478
� Types of Variables
Global Variables
What is a global variable?
• A global variable is a variable declared at the outermost level
of a program.
• They are declared outside any modules such as functions or
procedures
• Global variables have a global scope, which means they can
be accessed and modified from any part of the program
CS 0478
� Library Routines
ROUND(<Identifier>,<Places>)
Returns the value of the identifier rounded to places number of decimal
places. The identifier should be of data type real, places should be data
type integer.
Cost ← 1.9556
OUTPUT ROUND(Cost,2)
// Outputs 1.95
CS 0478
� Library Routines
RANDOM()
Returns a random number between 0 and 1 inclusive.
Value ← ROUND (RANDOM() * 6, 0)
// returns a whole number between 0 and 6
Value ← ROUND (RANDOM() * 6, 0)
// returns a whole number between 0 and 6
CS 0478