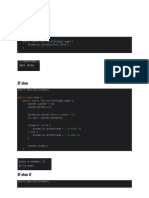
PROGRAM 1:
Write a program to to display the use of logical operators.
public class Logical1
public static void main(String args[])
int a=360, b=240, c=200;
//using logical AND, BUT, and NOT
System.out.println("a and b are both even numbers: "+((a%2==0)&&(b%2==0)));
System.out.println("a is greater than b or c: "+((a>b)||(a>c)));
System.out.println("a is not greater than b and c: "+!((a>b)&&(a>c)));
OUTPUT:
1
�VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
a int To input the first number
b int To input the second number
c int To input the third number
2
�PROGRAM 2:
Write a program to display () method of a class.
public class Student
void display()
String name="Rohan";
int age=30;
double salary=20000;
System.out.println("Name:"+name);
System.out.println("Age:"+age);
System.out.println("Salary:"+salary);
public static void main(String args[])
Student S1=new Student();//using the new operator to create object class
S1.display();//using the dot operator to access member function
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
Name string To input the name
Age int To input the age
Salary double To input the salary
3
�OUTPUT:
4
�PROGRAM 3:
import java.util.*;
public class Loan
int time;
double principal,rate,interest,amt;
public void getdata()
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter principal:");
principal=in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter time:");
time=in.nextInt();
public void calculate()
if (time<=5)
rate=15.0;
else if (time<=10)
rate=12.0;
else
rate=10.0;
interest=(principal *rate*time)/100.0;
amt=principal+interest;
public void display()
System.out.println("Interest="+interest);
System.out.println("Amount payable="+amt);
public static void main(String args[])
5
� {
Loan ob=new Loan();
ob.getdata();
ob.calculate();
ob.display();
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
time int To input the time period
principle double To input the principal
rate double To input the rate
interest double To input the time interest
amount double To calculate amount
6
�PROGRAM 4:
Write a program to find the square of the given number.
public class number
int sq(int a)
int s;
s=a*a;
return (s);
public static void main(String args[])
number n= new number ();
int x;
x=n.sq(5);
System.out.println("Square of 5 is:"+x);
OUTPUT:
7
�VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
a int To input the number
sq int To get the square of the number
s int To input the new number
8
�PROGRAM 5:
Design a class to overload a function polygon() to do following tasks.
public class overload
int i,j;
void polygon(int n, char ch)
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
System.out.print(ch);
System.out.println();
void polygon(int x,int y)
for(i=1;i<=x;i++)
for (j=1;j<=y;j++)
System.out.print('@');
System.out.println();
void polygon()
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
9
� for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
System.out.print('*');
System.out.println();
public static void main (String args[])
overload ob=new overload();
ob.polygon(4,'A');
ob.polygon(3,5);
ob.polygon();
OUTPUT:
10
�VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
i int To use in the loop
j int To use in the loop
11
�PROGRAM 6:
import java.util.*;
public class Upgrade
String name;
int bas,expn;
double inc,nbas;
Upgrade()//Default constructor
name="";
bas=0;
expn=0;
inc=0.0;
nbas-=0.0;
void accept()
Scanner input=new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.print("Enter name:");
name=input.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter basic:");
bas=input.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter experience:");
expn=input.nextInt();
public void increment()
if(expn<=3)
inc=1000+(bas*0.1);
else if(expn<=5)
inc=3000+(bas*0.12);
12
� else if (expn<=10)
inc=5000+(bas*0.15);
else
inc=8000+(bas*0.2);
nbas=bas+inc;
void display()
System.out.println("Name:"+name);
System.out.println("Basic:"+ bas);
System.out.println("Experiment:"+expn);
System.out.println("Increment:"+ inc);
System.out.println("New Basic:"+ nbas);
public static void main (String args[])
Upgrade ob = new Upgrade();
ob.accept();
ob.increment();
ob.display();
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
name String To store the name
bas int To store basic salaray
expn int To consider the length of service
inc double To store the increment
nbas double To store the basic salary
13
�OUTPUT:
14
�PROGRAM 7:
Write a program to define the class ‘Rectangle’ . Use the default instructor to initialise the
data members and invoke the constructor and methods in the main() method.
import java.util.*;
public class Rectangle
int l,b,a;
Rectangle()
l=0;
b=0;
a=0;
void input()
Scanner input=new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.println("Enter length and breadth");
l=input.nextInt();
b=input.nextInt();
void findarea()
a=l*b;
void display ()
System.out.println("Length="+l);
System.out.println("Breadth="+b);
System.out.println("Area="+a);
public static void main(String args [])
15
� {
Rectangle Ob=new Rectangle();
Ob.input();
Ob.findarea();
Ob.display();
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
length int To store length of the rectangle
breadth int To store breadth of the rectangle
area int To store area of the rectangle
16
�PROGRAM 8:
Create a class ‘Cuboid’ with data data members length,breadth, and height. Use a parameterised
constructor to initialise the object and two functions : surfacearea() and volume() to calculate the
surface area and volume of the cuboid.
import java.io.*;
public class cuboid
int l,b,h;
cuboid (int x,int y,int z)
l=x;
b=y;
h=z;
void findsurfacearea()
int a=2*(l*b+b*h+h*l);
System.out.println("Surface area =" +a);
void volume()
int v= l*b*h;
System.out.println("Volume="+v);
public static void main (String args[])
cuboid ob=new cuboid (5,7,9);
ob.findsurfacearea();
ob.volume();
17
� OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
pamt double To store principal amount
time int To store time period
amt double To store amount
rate double To store rate of interest
18
�PROGRAM 9:
Write a program that demonstrates the use of parsing methods.
public class parse
{
public static void main (String args [])
{
int x = Integer.parseInt("9");
float f = Float.parseFloat("123.45");
long l = Long.parseLong("9988776655");
double d = Double.parseDouble("3.14E10");
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println(l);
System.out.println(d);
}
}
OUTPUT:
19
� VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
f float To convert in float value
x int To convert in integer value
l long To convert in long value
d double To convert in double value
20
�PROGRAM 10:
Write a program to input 10 numbers in a single dimensional array. Find the largest, second
largest, and the smallest element of the array.
import java.util.*;
public class numbers
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
Scanner input= new Scanner(System.in);
int i,max,min,smax;
int n[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 numbers");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
n[i]=input.nextInt();
}
max=smax=min=n[0];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if(n[i]>max)
{
smax=max;
max=n[i];
}
if(n[i]>smax && n[i]<max)
{
smax=n[i];
}
if(n[i]<min)
{
21
� min= n[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Largest number is:"+max);
System.out.println("Second largest number is :"+smax);
System.out.println("Smallest number is:"+min);
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
max String For maximum number
min int For minimum number
i int For loop
smax char For second maximum number
22
�PROGRAM 11:
Write a program to input numbers in a 4 x 4 array. Check weather the matrix is symmetric or
not.
import java.util.*;
public class matrsym
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int i,j,k=0;
int n[][]=new int[4][4];
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
n[1][j]=input.nextInt();
}
}
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
if(n[i][j] != n[j][i])
{
k=1;
break;
}
}
23
� }
if(k==0)
System.out.print("Symmeric Matrix");
else
System.out.print("Not a Symmetric Matrix");
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
k String For loop
j int For loop
i int For loop
24
�PROGRAM 12:
Write a program to input 10 numbers in a single -dimensional array. Check weather the
element is present in the array or not using the binary search technique.
import java.util.*;
class bin_search1
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
Scanner input=new Scanner (System.in);
int i,lb=0,ub=9,m,ns,k=0;
int n[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the array elements in ascending order:");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
n[i]=input.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter a number to search:");
ns=input.nextInt();
while(lb<=ub)
{
m=(lb+ub)/2;
if(ns<n[m])
ub=m-1;
if(ns>n[m])
lb=m+1;
if(ns==n[m])
{
k=1;
break;
25
� }
}
if(k==1)
System.out.println("Number is available");
else
System.out.println("Number is not available");
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
k String For loop
j int For loop
i int For loop
26
�PROGRAM 13:
Write a program to input 10 numbers in a single -dimensional array. Using the selection sort
technique, arrange the elements of array in ascending order and display the sorted array.
import java.util.*;
class sel_sort1
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,j,min=0,t;
int n[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
n[i]=input.nextInt();
}
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
min=i;
for(j=i+1;j<10;j++)
{
if(n[j]<n[min])
min=j;
}
t=n[min];
n[min]=n[i];
n[i]=t;
}
System.out.println("Sorted array:");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
27
� {
System.out.println(n[i]);
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
t int
min int
j int For loop
i int For loop
28
�PROGRAM 14:
Write a program to input 10 names in a single-dimensional array. Using the selection sort
technique, arrange the names of array in ascending order and display the sorted array.
import java.util.*;
public class sel_sort2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,j,min=0;
String t;
String n[]=new String[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 names:");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
n[i]=input.nextLine();
}
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
min=i;
for(j=i+1;j<10;j++)
{
if(n[j].compareTo(n[min])<0)
min=j;
}
t=n[min];
n[min]=n[i];
n[i]=t;
}
System.out.println("Sorted array:");
29
� for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println(n[i]);
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
t String
min int
j int For loop
i int For loop
30
�PROGRAM 15:
Write a program to input 10 numbers in a single- dimensional array. Using the bubble sort
technique, arrange the elements of the array in ascending order and display the sorted array.
import java.util.*;
class bub_sort1
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,j,t;
int n[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for (i=0;i<10;i++)
{
n[i]=input.nextInt();
}
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<9-i;j++)
{
if(n[j]>n[j+1])
{
t=n[j];
n[j]=n[j+1];
n[j+1]=t;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Sorted array:");
31
� for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println(n[i]);
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
j int
j int For loop
i int For loop
32
�PROGRAM 16:
Write a program to input 10 names in a singe-dimensional array. Using the bubble sort
technique, arrange the names of the array in the descending order and display the sorted
array.
import java.util.*;
class bub_sort2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int i,j;
String t="";
String n[]=new String[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 names:");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
n[i]=input.nextLine();
}
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<9-i;j++)
{
if(n[j].compareTo(n[j+1])<0)
{
t=n[j];
n[j]=n[j+1];
n[j+1]=t;
}
}
33
� }
System.out.println("Sorted array in descending order:");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println(n[i]);
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
n String
t String
j int For loop
i int For loop
34
�PROGRAM 17:
Write a program to input a sentence and find the words that begin and end with the same
letter. Also, count the number of such words.
import java.util.*;
public class Count_Words
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s,w=" ";
int i,l,f=0;
char c,c1,c2;
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
s=input.nextLine();
s=s.toUpperCase();
s=s+" ";
l=s.length();
for(i=0;i<l;i++)
{
c=s.charAt(i);
if(c!=' ')
w=w+c;
else
{
c1=w.charAt(0);
c2=w.charAt(w.length()-1);
if(c1==c2)
{
System.out.println(w);
f++;
35
� }
w="";
}
}
System.out.println("The total number of words that begin and end with the same letter
is:"+f);
}
}
OUTPUT:
36
�VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
w String
s String For loop
f int
l int Length of String
i int For loop
c char
c1 char
c2 char
37
�PROGRAM 18:
Write program to input a sentence and find the number of vowels in it.
import java.util.*;
public class Count_Vowels
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
String s;
int i,l,v=0;
char c;
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
s=in.nextLine();
l=s.length();
for(i=0;i<l;i++)
{
c=s.charAt(i);
if(c=='A'||c=='E'|| c=='I'|| c=='U'|| c=='O'|| c=='a'|| c=='e'|| c=='i'|| c=='o' || c=='u')
v=v++;
}
System.out.println("Number of vowels are:"+v);
}
}
38
�OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
s String To input sentence
l int For the length of String
i int For loop
c char To return character’s index
v int To store vowels
39
�PROGRAM 19:
Write a program to input a sentence and reprint it after changing the case of
each letter.
import java.util.*;
public class chng_case
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner in=new Scanner (System.in);
String s,s1="";
int i,l;
char c;
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
s=in.nextLine();
l=s.length();
for(i=0;i<l;i++)
{
c=s.charAt(i);
if(Character.isUpperCase(c))
c=Character.toLowerCase(c);
else if(Character.isLowerCase(c))
c=Character.toUpperCase(c);
else
c=c;
s1=s1+c;
}
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
40
�OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
s String To input sentence
l int For the length of String
i int For loop
c char To return character’s index
41
�PROGRAM 20:
Write a program to input a sentence and reprint it after changing its case in
various forms.
import java.util.*;
public class Chng_Char
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s,s1="";
int i,l;
char c;
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
s=in.nextLine();
l=s.length();
for(i=0;i<l;i++)
{
c=s.charAt(i);
if(Character.isUpperCase(c))
c=Character.toLowerCase(c);
else if(Character.isLowerCase(c))
c=Character.toUpperCase(c);
else if(c==' ')
c='?';
else if(Character.isDigit(c))
c='#';
else
c='*';
s1=s1+c;
42
� }
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
OUTPUT:
VARIABLE DESCRIPTION TABLE:
Variable Type Description
s String To input sentence
l int For the length of String
i int For loop
c char To return character’s index
43