0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views9 pagesLecture 22 Radix Sort
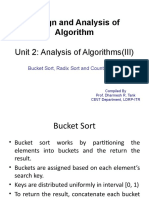
This document provides an overview of Radix Sort, including its advantages over traditional sorting algorithms and its complexity analysis. It explains the process of sorting names and numbers using Radix Sort, detailing the multiple passes required based on the number of digits. Additionally, it discusses the complexity in different cases, highlighting scenarios where the number of passes is significantly less than the number of elements.
Uploaded by
ranahassanirfan2005Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views9 pagesLecture 22 Radix Sort
This document provides an overview of Radix Sort, including its advantages over traditional sorting algorithms and its complexity analysis. It explains the process of sorting names and numbers using Radix Sort, detailing the multiple passes required based on the number of digits. Additionally, it discusses the complexity in different cases, highlighting scenarios where the number of passes is significantly less than the number of elements.
Uploaded by
ranahassanirfan2005Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9