0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views11 pagesJAVA This Keyword
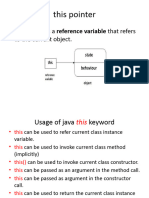
The document explains the usage of the 'this' keyword in Java, which refers to the current object in methods or constructors and helps eliminate confusion between class attributes and parameters with the same name. It outlines various methods to use 'this', including referring to instance variables, invoking constructors, and passing the current object as a parameter. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using 'this' in Java programming.
Uploaded by
gopogo56Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views11 pagesJAVA This Keyword
The document explains the usage of the 'this' keyword in Java, which refers to the current object in methods or constructors and helps eliminate confusion between class attributes and parameters with the same name. It outlines various methods to use 'this', including referring to instance variables, invoking constructors, and passing the current object as a parameter. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using 'this' in Java programming.
Uploaded by
gopogo56Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11