0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views9 pagesKubectl Commands
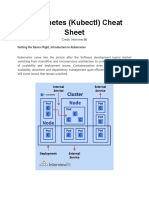
The document provides a comprehensive guide on various Kubernetes commands and configurations, including node management, deployment, and resource monitoring. It covers essential paths, SSL certificate management, and methods for upgrading nodes, as well as detailed instructions for managing pods, services, and secrets. Additionally, it includes troubleshooting commands and information on service accounts and Docker registries.
Uploaded by
winter2022seCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views9 pagesKubectl Commands
The document provides a comprehensive guide on various Kubernetes commands and configurations, including node management, deployment, and resource monitoring. It covers essential paths, SSL certificate management, and methods for upgrading nodes, as well as detailed instructions for managing pods, services, and secrets. Additionally, it includes troubleshooting commands and information on service accounts and Docker registries.
Uploaded by
winter2022seCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9