2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Network Fundamentals II
All Lessons Structure
Introduction to Network Fundamentals 2
Basic Concepts
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Network Protocols
OSI Reference Model
Media Access Control (MAC) Address
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Internet Protocol (IP)
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Routing
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 1/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Basic Concepts
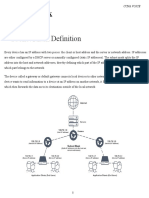
Unicast
“Unicast” is transmitting network packets to a single destination in the network. If a single
system transmits network packets to a single destination it is called Unicast.
Note: Each colored circle in the image below represents a device in the network.
Multicast
“Multicast”, is transmitting network packets to a multiple destinations within the same
network.
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 2/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
Broadcast
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
“Broadcast”, is when a device in the network transmits network packets to all devices in the
network.
Broadcast Domain
“Broadcast domain”, refers to each separate network, usually separated by routers.
Broadcast domains refer to the areas that broadcast messages can reach. Switches can also
be used with some configurations (VLANs) to specify broadcast domains.
Note: VLAN will be covered later in the training.
The image above shows a topology of two separate networks connected to two interfaces of
a router. Each interface of the router constitutes the entire broadcast domain. The router
above has two interfaces, so there are two different broadcast domains.
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 3/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
Collision Domain
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
“Collision domain”, are usually much smaller domains than broadcast domains. Collision
domains are areas that can cause collisions between packets using the same data path. For
example, since packets coming from one port of the hub are sent to all other ports, all ports
of the hub device as a whole form a collision domain. On the other hand the switches are a
little different. Since the switches transmits target-oriented packets each port of the switches
creates a separate collision domain.
Each green area in the image above represents a separate collision domain.
Subnet Mask
What is Subnet Mask?
Subnet mask is an address used to detect network addresses and to separate networks into
subnets. While assigning IP address to every single device in the network subnet mask
assignment should also be made because devices cannot find network addresses without
subnet mask. If the network address cannot be found it is not possible to transmit packets.
In short, communication between devices can’t be established. The subnet mask is 4 bytes
long, just like the IPv4 address, and is expressed in decimal notation. For example, the
following is a subnet mask:
Example Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.0
Default Subnet Masks
Subnet masks have a default value for each IP address class:
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 4/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
The table above shows the default subnet masks for each IP address class. Another
representation of subnet masks is the "prefix" representation. In prefix notation, the number
of “1” bits in the subnet mask is specified. These “1” bits are in left-to-right order. In prefix
notation, the number of bits is written with the “/” sign. For example, the binary
representation of the “/8” subnet mask is as follows:
/8 = 11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000
In this example, the 8 bits from the left of the 32 bits representing the subnet mask shows
the "1" bit, and all the remaining bits shows the "0" bit.
All subnet masks and prefix representations are shown in the table below:
Bitwise AND Operation
AND is one of the operations performed on the bits. The results of AND operations on the
bits are shown in the table below:
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 5/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
Finding the Network AddressHomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Bitwise AND operation is used to determine the network address with the subnet mask. The
IP address and the subnet mask are ANDed. The result obtained gives the network address.
For example, let's perform an AND operation on an IP address and subnet mask as follows:
IP Address (Decimal) : 192.168.3.100
IP Address (Binary) : 11000000.10101000.00000011.01100100
Subnet Mask (Decimal) : 255.255.255.0
Subnet Mask (Binary) : 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
As seen in the image above, each bit of 32 bits belonging to the IP address and subnet mask
was sequentially ANDed and the network address was obtained as "192.168.3.0".
We have covered the basic concepts of the network as well as the subnet mask topics. We
have learned how the subnet mask and network address are calculated. We will cover
“Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)” in the next part of the training.
Lab Environment
Questions Progress
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 6/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Correct
According to the image above, what is the name of the transmission type of network packet #1?
Answer Format: word
unicast Completed
Hint
Correct
According to the image above, what is the name of the transmission type of network packet #2?
Answer Format: word
broadcast Completed
Hint
Correct
According to the image above, what is the name of the transmission type of network packet #3?
Answer Format: word
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 7/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
multicast Completed
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Hint
Correct
NOTE: All switches in the above topology are dummy switches and do not have VLAN features.
NOTE: Please answer the following first 4 questions according to the image above.
How many of the green areas numbered in the image above are broadcast domains?
Answer Format: number
Sample Answer: 1
5 Completed
Hint
Correct
According to the image above, how many of the following statements are true?
All broadcast domains in the topology are located within the numbered green areas.
There are collision domains in the topology that are not numbered and are not green.
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 8/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
Areas 1, 2, and 3 are broadcast domains.
Area 4 is the collision domain.
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Area 7 is the collision domain.
Area 5 is the collision domain.
Answer Format: number
Sample Answer: 1
4 Completed
Hint
Correct
How many of the numbered areas above are collision domains?
Answer Format: number
Sample Answer: 1
5 Completed
Hint
Correct
Which area above is not both a collision domain and a broadcast domain?
Answer Format: number
Sample Answer: 1
6 Completed
Hint
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 9/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
What is the subnet mask of the "Ethernet" interface of the Windows system?
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
Note: You need to connect to the machine.
Answer Format: X.X.X.X
Answer Format: ***.***.***.* Submit
Hint
Back Next
LetsDefend
Social
Resources
Support
Community
Plans
Roles
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 10/11
�2/5/24, 11:28 PM Basic Concepts - LetsDefend
HomeLearnPracticeChallengePricing
https://app.letsdefend.io/training/lesson_detail/basic-concepts-network-fundamentals-ii 11/11