100% found this document useful (4 votes)
78 views3 pagesScience SSP Paper
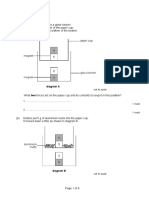
The document outlines a Year 7 science paper focused on electricity, covering basic concepts, circuit diagrams, current, voltage, resistance, series and parallel circuits, safety precautions, and energy and power. It includes instructions for writing and specific questions to assess understanding of the topic. The paper is structured into easy, medium, and hard levels, providing a comprehensive overview of electricity for students.
Uploaded by
Anbu SelvanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (4 votes)
78 views3 pagesScience SSP Paper
The document outlines a Year 7 science paper focused on electricity, covering basic concepts, circuit diagrams, current, voltage, resistance, series and parallel circuits, safety precautions, and energy and power. It includes instructions for writing and specific questions to assess understanding of the topic. The paper is structured into easy, medium, and hard levels, providing a comprehensive overview of electricity for students.
Uploaded by
Anbu SelvanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3