**This study guide is based on the video lesson available on TrainerTests.
com**
Understanding Amazon EKS and Fargate for Container
Orchestration Study Guide
This chapter dives into container orchestration on AWS, focusing on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes
Service (EKS) and Fargate. It explains the concepts behind Kubernetes, explores the challenges of
self-managed deployments, and highlights the benefits of EKS and Fargate.
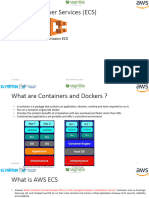
Introduction to Container Orchestration
Containerization is a popular approach to deploying applications. Containers package applications
with their dependencies, allowing them to run consistently across different environments. However,
managing multiple containers at scale requires orchestration. Container orchestration automates
container deployment, scaling, and management.
Challenges of Self-Managed Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a leading open-source container orchestration platform. While powerful, setting up and
maintaining a self-managed Kubernetes cluster on AWS can be complex. Here's what's involved:
• Multi-AZ Deployment: For high availability, a Kubernetes cluster should span multiple
Availability Zones (AZs) within an AWS region. This ensures that if one AZ fails, the cluster
remains operational.
• Control Plane Management: The Kubernetes control plane consists of master nodes and
etcd instances. These manage the worker nodes and container lifecycles. Manually
provisioning and maintaining these components is a significant burden.
• Worker Node Management: Worker nodes are EC2 instances that run containers. You need
to create and manage these instances, including scaling them based on workload demands.
• Failure Handling: Kubernetes requires mechanisms to handle node failures and automatically
reschedule containers on healthy nodes.
EKS: Managed Kubernetes on AWS
Amazon EKS simplifies container orchestration by offering a managed Kubernetes service. Here's
how it addresses the challenges:
� • Automated Control Plane: EKS eliminates the need to manually manage the control plane. It
automatically provisions and maintains the master nodes and etcd instances, ensuring a highly
available control plane.
• Simplified Worker Node Management: While you still need to create worker nodes as EC2
instances, EKS simplifies the process. It can be done through the EKS console or API calls.
EKS also automatically detects and replaces unhealthy control plane nodes.
• Open Source Compatibility: EKS uses upstream Kubernetes software. This ensures
compatibility with existing Kubernetes plugins and tooling, allowing you to leverage your
existing knowledge and resources.
Fargate: Serverless Compute for Containers
Fargate is a serverless compute service from AWS that integrates with EKS. It eliminates the need to
manage worker nodes altogether. Here's what Fargate offers:
• Serverless Worker Nodes: Fargate provides on-demand, serverless compute resources for
running your containers. You don't need to provision, configure, or scale EC2 instances for
worker nodes.
• Resource Efficiency: With Fargate, you define the resource requirements (CPU, memory) for
each container. You only pay for the resources your containers use, leading to cost
optimization.
• Simplified Management: Fargate eliminates the complexities of managing worker nodes,
including scaling, patching, and failure handling. This frees up your time to focus on application
development.
EKS with Fargate: A Fully Managed Solution
Combining EKS and Fargate provides a truly managed solution for container orchestration on AWS.
• Reduced Operational Overhead: EKS takes care of the control plane, and Fargate manages
the worker nodes. This significantly reduces the operational overhead associated with running
a Kubernetes cluster.
• Focus on Applications: By eliminating worker node management, EKS with Fargate allows
developers to focus on building and deploying applications instead of infrastructure
management.
Conclusion
EKS and Fargate offer a compelling solution for container orchestration on AWS. EKS simplifies
Kubernetes management, while Fargate provides serverless compute for worker nodes. Together,
they reduce operational overhead and allow developers to focus on building and deploying scalable
containerized applications.
*See slides below: