0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views43 pagesAcceptability of String - Transition Graph
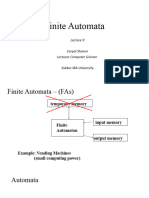
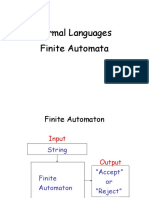
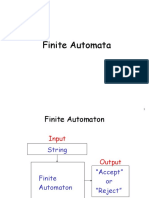
The document discusses finite automata, focusing on the acceptability of strings and the properties of transition functions. It includes examples of input strings that are accepted or rejected by the finite automaton, as well as the definition of languages accepted by finite automata. Additionally, it covers the transition function and its recursive definition for processing input strings.
Uploaded by
Aman Kumar SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views43 pagesAcceptability of String - Transition Graph
The document discusses finite automata, focusing on the acceptability of strings and the properties of transition functions. It includes examples of input strings that are accepted or rejected by the finite automaton, as well as the definition of languages accepted by finite automata. Additionally, it covers the transition function and its recursive definition for processing input strings.
Uploaded by
Aman Kumar SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 43