0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views44 pagesCOL726 Lecture Notes 6
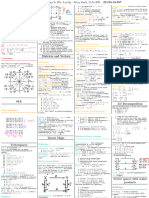
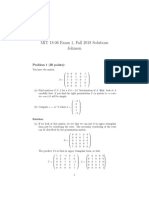
The document discusses numerical algorithms and mathematical problems related to function evaluation, optimization, and error analysis, including absolute and relative errors. It covers concepts of conditioning, stability, floating-point arithmetic, and various norms in linear algebra, including singular value decomposition and QR factorization. Additionally, it addresses the implications of these mathematical concepts in computational contexts and their applications.
Uploaded by
amansinghdalawatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views44 pagesCOL726 Lecture Notes 6
The document discusses numerical algorithms and mathematical problems related to function evaluation, optimization, and error analysis, including absolute and relative errors. It covers concepts of conditioning, stability, floating-point arithmetic, and various norms in linear algebra, including singular value decomposition and QR factorization. Additionally, it addresses the implications of these mathematical concepts in computational contexts and their applications.
Uploaded by
amansinghdalawatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 44