0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesGeneral: Temp, Light, Privacy, Equipment Eg Inhaler, Nasal Prong, Prong, IV Line, Stomal, Foley S Catheter, Wheel Chair
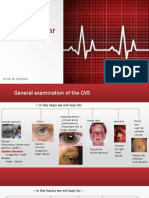
The document outlines the procedure for conducting a cardiovascular (CVS) examination, including patient positioning, general observations, and specific assessments of vital signs and pulses. It details inspection techniques for various body parts, palpation methods, and auscultation of heart valves, along with important clinical signs to note. The document emphasizes the importance of thorough examination and patient interaction throughout the process.
Uploaded by
LANA ASS'ADCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesGeneral: Temp, Light, Privacy, Equipment Eg Inhaler, Nasal Prong, Prong, IV Line, Stomal, Foley S Catheter, Wheel Chair
The document outlines the procedure for conducting a cardiovascular (CVS) examination, including patient positioning, general observations, and specific assessments of vital signs and pulses. It details inspection techniques for various body parts, palpation methods, and auscultation of heart valves, along with important clinical signs to note. The document emphasizes the importance of thorough examination and patient interaction throughout the process.
Uploaded by
LANA ASS'ADCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6