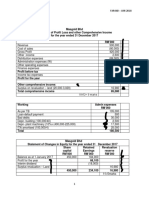
FRM Concepts Overview
explain all concepts of FRM
The Financial Risk Manager (FRM) certification is a globally recognized credential for
professionals in the field of risk management. It focuses on identifying, analyzing, and
mitigating financial risks in various industries. The FRM syllabus covers a wide range of
concepts and topics within financial risk management, including the following core areas:
1. Foundations of Risk Management
Risk Management Frameworks: This covers the basic structure of risk management,
including the identification, measurement, and mitigation of risks.
Risk Types: Understanding different types of risk is fundamental. These include:
Market Risk: The risk of losses due to changes in market prices (e.g., interest rates,
exchange rates, stock prices).
Credit Risk: The risk that a counterparty will default on a financial obligation.
Operational Risk: The risk of loss from failed internal processes, systems, people, or
external events.
Liquidity Risk: The risk that a firm will not be able to meet its short-term financial
obligations due to the inability to convert assets into cash quickly.
Legal and Regulatory Risks: Risks related to legal and compliance issues.
2. Quantitative Analysis
Statistics and Probability: These are essential tools for measuring risk, with concepts
like mean, standard deviation, variance, correlation, and regression analysis.
Risk and Return: Understanding the relationship between risk and potential returns,
including measures like Sharpe Ratio, Value at Risk (VaR), and expected shortfall.
Portfolio Theory: Examines the construction of optimal portfolios and diversification,
using tools such as the efficient frontier, Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), and Modern
Portfolio Theory (MPT).
Monte Carlo Simulation: A technique used for risk analysis through the use of random
sampling to compute results and assess uncertainty.
3. Financial Markets and Products
1/4
� Financial Instruments: A broad understanding of financial products such as stocks,
bonds, derivatives (options, futures, swaps), and their risk profiles.
Derivatives: These financial instruments are crucial for risk management and include
instruments like options, futures, and forward contracts, often used for hedging
purposes.
Securitization: The process of pooling and repackaging financial assets to create new
securities, such as mortgage-backed securities (MBS).
4. Market Risk Measurement and Management
Risk Measurement Models: Analyzing market risk using models like Value at Risk (VaR),
Conditional VaR (CVaR), and stress testing.
VaR Techniques: Discusses how VaR is used to measure the potential loss in value of a
portfolio due to adverse market movements. Different methods, such as historical
simulation, Monte Carlo simulation, and parametric approaches, are explored.
Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis: Techniques to understand how extreme market
conditions could affect a portfolio.
5. Credit Risk Measurement and Management
Credit Risk Analysis: Understanding how to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers or
counterparties.
Credit Derivatives: Instruments like credit default swaps (CDS) that can be used to
transfer or hedge credit risk.
Credit Valuation Models: Tools for assessing the likelihood of default, including the use
of credit ratings, credit spreads, and structural models like the Merton model.
Credit Portfolio Management: Techniques for managing the credit risk associated with
large portfolios of loans, bonds, or other credit exposures.
6. Operational and Integrated Risk Management
Operational Risk: The risk of loss due to inadequate or failed internal processes,
systems, or external events (e.g., natural disasters, fraud).
Risk Control and Mitigation: Methods to reduce operational risk, including developing
internal controls, contingency planning, and crisis management.
2/4
� Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): A holistic approach to managing all types of risk
across an organization, integrating risk into the strategic and operational framework.
Risk Governance: Establishing a governance framework for risk management at an
organizational level.
7. Risk Management and Investment Management
Hedging Strategies: Use of derivatives and other instruments to manage risk exposure
in investment portfolios.
Asset and Liability Management (ALM): The management of financial risks that arise
due to mismatches between assets and liabilities, often relevant in banking and
insurance.
Capital Adequacy: Understanding the capital requirements necessary to support the
risk exposures of a financial institution, often in the context of regulatory requirements
like Basel III.
8. Current Issues in Financial Markets and Risk Management
Financial Crises and Systemic Risk: Understanding the causes and consequences of
financial crises, including systemic risks and how they can be managed.
Regulation and Compliance: Knowledge of the legal and regulatory frameworks that
govern risk management practices, including international standards like Basel III and
Dodd-Frank.
Climate and ESG Risks: Increasing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG)
risks, as well as the financial risks associated with climate change.
9. Risk Management in Banks and Other Financial Institutions
Banking Risks: Specific risks faced by banks, including credit risk, liquidity risk, interest
rate risk, and operational risk.
Stress Testing: The application of stress tests and scenario analysis to assess the ability
of banks to withstand adverse economic conditions.
Regulatory Capital and Liquidity Requirements: Understanding the rules and
standards set by regulatory bodies (e.g., Basel III) to ensure financial institutions
maintain adequate capital buffers and liquidity.
10. Valuation and Risk Management in Financial Products
3/4
� Pricing and Valuation of Derivatives: Using models like the Black-Scholes model for
options pricing and other methods for pricing futures and swaps.
Risk Adjusted Return: Techniques for measuring return on investment adjusted for the
level of risk undertaken, using metrics like the Sharpe ratio.
These topics are essential for professionals who work in risk management roles across
various industries, including banking, insurance, investment, and corporate finance. The FRM
certification requires a deep understanding of financial theory, quantitative techniques, and
practical applications of risk management tools. Would you like more detail on any specific
area?
4/4