0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views3 pagesImportant Topics
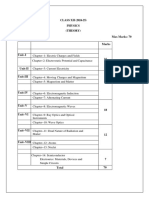
The document outlines key concepts in physics, covering electrostatics, current electricity, magnetism, electromagnetic induction, optics, dual nature of radiation, atomic structure, and electronic devices. It includes fundamental laws, principles, and applications related to electric charges, fields, circuits, magnetic effects, light behavior, and semiconductor technology. Each unit is divided into chapters that detail specific topics, formulas, and qualitative treatments of various phenomena.
Uploaded by
rashadakhatoon988Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views3 pagesImportant Topics
The document outlines key concepts in physics, covering electrostatics, current electricity, magnetism, electromagnetic induction, optics, dual nature of radiation, atomic structure, and electronic devices. It includes fundamental laws, principles, and applications related to electric charges, fields, circuits, magnetic effects, light behavior, and semiconductor technology. Each unit is divided into chapters that detail specific topics, formulas, and qualitative treatments of various phenomena.
Uploaded by
rashadakhatoon988Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3