0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views5 pagesELK Stack For DevOps
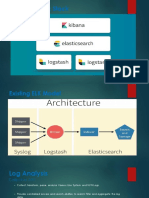
The ELK Stack consists of Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana, which together enable real-time log data searching, analyzing, and visualization essential for DevOps. The document provides a step-by-step guide for installing and configuring each component on a Linux system, including prerequisites, installation commands, and configuration settings. It also covers optional security measures and advanced setups for enhanced functionality and reliability in log management and data analysis.
Uploaded by
antaralaerospaceCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views5 pagesELK Stack For DevOps
The ELK Stack consists of Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana, which together enable real-time log data searching, analyzing, and visualization essential for DevOps. The document provides a step-by-step guide for installing and configuring each component on a Linux system, including prerequisites, installation commands, and configuration settings. It also covers optional security measures and advanced setups for enhanced functionality and reliability in log management and data analysis.
Uploaded by
antaralaerospaceCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5