NumPy Cheat Sheet for Python Data Science
Uploaded by
Tushar GoelNumPy Cheat Sheet for Python Data Science
Uploaded by
Tushar Goel> Inspecting Your Array > Sorting Arrays
Python For Data Science
>>>
>>> a.shape #Array
a.shape #Array dimensions
dimensions >>>
>>> a.sort()
a.sort() #Sort
#Sort an
an array
array
>>>
>>> len(a)
Llen(a) #Length
#Length ofof array
array
>>> c.sort(axis=0) #Sort the elements of an array's axis
>>>
>>> b.ndim
b.ndim # Number of
#Number of array
array dimensions
dimensions
NumPy Cheat Sheet
>>>
>>> e.si ze #
e.size Number of
#Number of array
array elements
elements
>>> b.dtype
b.dtype # Data type
type of
of array
array elements
> Subsetting, Slicing, Indexing
>>> #Data elements
*
>>>
>>> b.dtype.name
b.dtype.name # Name of
#Name of data
data type
type
>>> b.astype(int) #Convert an array to a different type
Learn
Learn NumPy
NumPy online
online at
at www.DataCamp.com
www.DataCamp.com Subsetting
Subsetting
> Data Types >>>
>>> a
35
>>>
>>> b
[2] #Select
al[2] #Select the
[1,2] #Select
b[1,2]
the element
element at
#Select the
at the
the element
element at
the 2nd
at row 1
row
index
2nd index
1 column
column 2 equivalent to
2 ((equivalent to b[1][2])
b[1][2])
1
1.5 2
2 3
3
6.
6.0 0 4 5 6
>>>
>>> np.int64
np.int64 #Signed
#Signed 64-bit
64-bit integer
integer types
types
Numpy
>>>
>>> np.float32
np.float32 #Standard
#Standard double-precision floating point
double-precision floating point
Slicin
Slicingg
>>>
>>> np.complex
np.complex #Complex
#Complex numbers
numbers represented
represented by
by 128 floats
128 floats >>>
>>> a[0:2] #Select
a[0:2] #Select items
items at index 0
at index 0 and
and 1
1 1 2 3
>>>
>>> Numpy
np.bool
np.bool #Boolean
#Boolean type
type storing
storing TRUE
TRUE and
and FALSE
FALSE values
values array( [1, 2
array([1, ])
2])
>>>
>>> np.object
np.object #Python
#Python object
object type
type >>>
>>> b[0:2,1] #Select
b[0:2,1] #Select items
items atat ro ws 0
rows 0 and
and 1 in column
1 in column 1
1 1.5 2 3
>>> np.string_
np.string_ #Fixed-length
#Fixed-length string
string type
The
The NumPy
NumPy lilibrary
brary is
is the
the core lilibrary
core brary ffor
or sscientific
cientific c omputing iin
computing n
Python
Python..
>>>
>>>
type
np.unicode_ #Fixed-length unicode type
array(
array([[ 2.,
2., 5 .])
5.]) 4 5 6
>>>
>>> b[:1] #Select
#Select allall items
items at
at ro w 0 equivalent to
0 ((equivalent to b[0:1, :])
IItt provides aa high performance multidimensional
multidimensional a rray object, and
and tools or b[:1] row b[0:1, :])
provides high-performance array object, tools ffor array( [[1.5, 2.,
array([[1.5, 2., 3. ]])
3.]])
1.5 2 3
4 5 6
w orking w
working ith these
with these a rrays
arrays >>>
>>> c[1,...] #Same
c[1,...] #Same asas [ 1,:,:]
[1,:,:]
> Array Mathematics
array( [[[ 3.,
array([[[ 3., 2.,
2., 1 .],
1.],
Use the
Use ollowing import
the ffollowing import convention:
convention: [[ 4.,
4., 5 ., 6.
5., ]]])
6.]]])
>>> a[[ :: ::-1]
>>> a -1] #Reversed
#Reversed arrayarray a a array ([3, 2
array([3, 2,, 1])
1])
>>>
>>> import
import numpy
numpy as
as np
np
BBoolean
oolean IIndexing
ndexing
Ar ithmetic O
Arithmetic perations
Operations >>>
>>> a[a<2] #Select
ala<2] #Select elements from aa less
elements from less than
than 2
2 1 2 3
NumPy
NumPy Arrays
Arrays array([1])
array([1])
>>>
>>> g
g =
= aa - bb #Subtraction
#Subtraction Fancy IIndexing
Fancy ndexing
array([[-0.5, 0
array([[-0.5, 0.. ,, 0
0.. ]J,,
>>>
>>> bb[[1,
[[1, 00,, 11,, 0] ,[0, 11,, 2,
0],[0, 0]] #Select
2, 0]] #Select elements 1,0),(
elements ((1,0), 0,1),(1,2) and
(0,1),(1,2) 0,0)
and ((0,0)
1D array 2D array [- 3. ,, -3.
[-3. 3. ,, -3.3. ]]]]))
array(
array([[ 4.
4. ,, 2.2. ,, 6.
6. ,, 1 .5])
1.5])
>>>
>>> np.subtract(a,b)
np.subtract(a,b) #Subtraction
#Subtraction
>>>
>>> b [[1, 0
b[[1, 0,, 11,, 0]][ :,[0,1,2,0]] #S#Select
OJIJ[:,[0,1,2,0]] elect aa subset
subset of
of the matrix
the ’s ro
matrix’s ws and
rows and column s
columns
>>>
>>> b + a
b + a #Addition
#Addition
array( [[ 4.
array([[ 4. ,,5.
5. ,, 6.
6. ,, 4.
4. ]J,,
array([[ 2.
array([[ 5, 4.
2.5, 4. ,, 6.
6. ]],,
[[ 1.5, 2.
1.5, 2. ,, 3.
3. ,, 1 .5],
1.5],
[ 5. , 7. , 9. ]]
[5.,7.,9. ]] )
[ 4. ,, 55.. ,, 6.
[4. 6 ,, 4.4. ]],,
>>>
>>> np.add(b,a)
np.add(b,a) Addition
Addition
[ 1.5, 2. , 3. , 1.5]])
>>>
>>> a
a / bb #Division
#Division
array([[ 0
array([[ .66666667, 11.. ,, 11.. ]J,,
0.66666667,
0.25 ,, 0
[[0.25 .4 , 00.5
0.4, .5 ]]]]))
>>>
>>> np.divide(a,b)
>>>
np.divide(a,b) #
>>> a
a * bb #
Division
#Division
Multiplication
#MuLtiplication > Array Manipulation
> Creating Arrays
array([[ 1
array([[ .5, 4.
1.5, 4. ,, 99.. ]],,
[ 4. ,, 10
[4. 10.. ,, 18 . ]]
18. ]]))
>>>
>>> np.multiply(a,b)
np.muLltiply(a,b) # Multiplication
#MulLtiplication TTransposing
ransposing A rray
Array
>>>
>>> np.exp(b)
np.exp(b) #Exponentiation
#Exponentiation
>>> i == np.transpose(b)
>>> i np.transpose(b) #Permute
#Permute array
array dimensions
dimensions
>>>
>>> aa =
= np.array([1,2,3])
np.array([1,2,3]) >>>
>>> np.sqrt(b) #S
np.sqrt(b) quare root
#Square root >>>
>>> i.T #Permute
1.T #Permute array
array dimensions
dimensions
>>>
>>> bb =
= np.array([(1.5,2,3), (4,
np.array([(1.5,2,3), 5,6)], dtype
(4,5,6)], dtype =
= float)
float) >>>
>>> np.sin(a)
np.sin(a) #Print
#Print sines
sines of of an
an array
array
>>>
>>> cc =
= np.array([[(1.5,2,3), (4,
np.array([[(1.5,2,3), 5,6)],[(3,2,1), (4,
(4,5,6)],[(3,2,1), 5,6)]], dtype
(4,5,6)]], dtype =
= float)
float) >>>
>>> np.cos(b)
np.cos(b) #Element- wise cosine
#Element-wise cosine Changing A
Changing rray Shape
Array Shape
>>>
>>> np.log(a)
np.log(a) #Element- wise natural
#Element-wise natural logarithm
logarithm
>>>
>>> b.ravel()
b.ravel() #Flatten
#Flatten the
the array
array
>>>
>>> e.dot(f)
e.dot(f) # Dot product
#Dot product
>>>
>>> g.res #Reshape,, but
hape(3, 2) #Reshape
g.reshape(3,-2) but don’t change
don’t change data
data
nitial Pla
IInitial ceholders
Placeholders array([[ 7
array([[
[[ 7
., 7
7.,
., 7
7.,
.],
7.],
.]])
7.]]) Adding/Removing EElements
Adding/Removing lements
>>>
>>> h .resize((2,6)) #Return
h.resize((2,6)) #Return a a ne
neww array
array w ith shape
with 2,6)
shape ((2,6)
>>>
>>> np. zeros((3,4)) #Create
np.zeros((3,4)) #Create an
an array
array of
of z eros
zeros >>>
>>> np.append( h,g) #Append
#Append items
items to to an
an array
Comparison
np.append(h,g) array
>>>
>>> np.ones((2,3,4),dtype=np.int
np.ones((2,3,4),dtype=np.int16) 16) #Create
#Create an
an array
array of
of ones
ones Comparison >>>
>>> np.insert(a,
np.insert(a, 11,, 5
5)) #Insert items
#Insert in an
items in an array
array
>>>
>>> d
d =
= np.arange( 10,25,5) #Create
np.arange(10,25,5) #Create an
an array
array of
of evenly
evenly spaced
spaced values step value
values ((step value))
>>>
>>> np.delete(a, [1]) #
np.delete(a,[1]) Delete items
#Delete from an
items from an array
array
>>>
>>> np.linspace( 0,2,9) #Create
np. linspace(0,2,9) #Create anan array
array of
of evenly
evenly spaced
spaced values number of
values ((number of samples
samples))
>>>
>>> e
e =
= np.full((2,2), 7) #Create
np.full((2,2),7) #Create aa constant
constant array
array >>>
>>> a = b
a == b #Element- wise comparison
#ELement-wise comparison Combining A
Combining rrays
Arrays
>>>
>>> f
f =
= np.eye(2)
np.eye(2) #Create
#Create aa 2X2 identity
2X2 identity matrix
matrix
array([[False, T
array([[False, rue, TTrue],
True, rue],
>>>
>>> np.concatenate((a,d),axis=
np.concatenate((a,d),axis=0) 0) #Concatenate
#Concatenate arrays
arrays
>>>
>>> np.random.random((2,2))
np.random.random((2,2)) #Create
#Create an
an array
array w ith random
random values
False, F
[[False, alse, FFalse]],
False, alse]], dtype=bool)
dtype=bool)
with values array(
array([[ 11,, 2,
2, 3,
3, 1010,, 15
15,, 2 0])
20])
>>>
>>> np.empty((3,2))
np.empty((3,2)) #Create
#Create an
an empty
empty array
array >>>
>>> a < 2
a < 2 #Element- wise comparison
#Element-wise comparison
>>>
>>> np.vstac k((a,b)) #Stac
np.vstack((a,b)) #Stack k arrays
arrays vertically row wise)
vertically ((row-wise)
array([True, F
array([True, alse, FFalse],
False, alse], dtype=bool)
dtype=bool) array([[ 1
array([[ 1.. ,, 2.
2. ,, 3.
3. ]],,
>>>
>>> np.array_e qual(a, b)
np.array_equal(a, b) #Array- wise comparison
#Array-wise comparison [[ 1 .5, 2.
1.5, 2. ,, 3.
3. ]],,
[[ 4.
4. , 5. , 6. ]] )
> I/O
,5., 6 ]]
>>>
>>> np.r_ [e,f] #Stac
np.r_Le,f] #Stack k arrays
arrays vertically row wise)
vertically ((row-wise)
Aggregate Fun
Aggregate ctions
Functions >>>
>>> np.hstack((e,f)) #Stac
np.hstack((e,f)) #Stack k arrays
arrays hori zontally ((column-wise)
horizontally column-wise)
array([[ 7
array([[ ., 77.,
7., ., 1 ., 00.],
1., .],
., 77.,
., 0@.,
., 1 .]])
Saving & Loading On Disk
[[ 7
7., 1.]])
>>>
>>> a.sum() #Array-wise sum
a.sum() >>>
>>> np.column_stac k((a,d)) #Create
np.coLumn_stack((a,d)) #Create stac ked column-
stacked wise arrays
column-wise arrays
>>>
>>> a.min() #Array-wise minimum
a.min() value
minimum value array([[ 1
array([[ 1,, 10]
10],,
>>>
>>> b.max(axis=0) #Maximum value
b.max(axis=0) value of an array row
[[ 2, 15],,
2, 15]
>>>
>>> np.save('my_array', a)
np.save('my_array', a) >>>
>>> b.cumsum(axis=1) #Cumulative sum
b.cumsum(axis=1) sum of the elements
[[ 3,
3, 2 0]])
20]])
>>>
>>> np.savez( 'array.npz', a,
np.savez('array.npz', a, b)
b) >>>
>>> a.mean()
a.mean() #Mean
>>>
>>> np.c_ [a,d] #Create
np.c_La,d] #Create stac
stackedked column- wise arrays
column-wise arrays
>>>
>>> np.load('my_array.npy')
np. Load('my_array.npy') >>>
>>> np.median(b) #Median
np.median(b) #Median
>>>
>>> np.corrcoef(a) #Correlation coefficient
np.corrcoef(a) Splittnp.vsplit(c,2)
ing A
Splitting
>>>
array([[[
[array([[[ rray
Arrayss1.5,2.,
[array([1]),array([2]),array([3])]
np.hsplit(a,3)
[ [4.
3.,
4., 5.
, 2.
5. #Split
, 6.
1. ]]]),
],the array horizontally
vertically at at
thethe2nd
3rd
index
index
>>>
>>> np.std(b) #Standard deviation
np.std(b) >>> np.hsplit(a,3) #Split the array horizontally at the 3rd index
Saving
saving
>>>
np. &
& Loading
Loading Text Files
np.genfromtxt("my_file.csv",
np.savetxt("myarray.txt",
lLoadtxt("myfile.txt")
Text
a, delimiter="
delimiter=',
Files ')") [array([1]),array([2]),array([3])]
>>> np.vsplit(c,2) #Split the array vertically at the 2nd index
> Copying Arrays
[array([[[ 1.5, 2. , 1. ],
>>> np.loadtxt("myfile.txt")
[ 4. , 5. , 6. ]]]),
>>> np.genfromtxt("my_file.csv", delimiter=',')
array([[[ 3., 2., 3.
5 ],
>>> np.savetxt("myarray.txt", a, delimiter=" ") [ 4., 5.,, 6.
©. ]]])]
>>>
>>> hh =
= a.view() #Create
a.view() #Create a
a view of
view of the
the array
array with the
with the same
same data
data
>>>
>>> np.copy(a)
np.copy(a) #Create
#Create a
a copy
copy of
of the
the array
array
> Asking For Help
>>>
>>> hh =
= a.copy()
a.copy() #Create
#Create a
a deep
deep copy
copy of
of the
the array
array
Learn Data Skills Online at www.DataCamp.com
>>>
>>> np.info(np.ndarray.dtype)
np.info(np.ndarray.dtype)
You might also like
- Arrays - Matrices and Vectors in Matlab, Freemat, Octave and Scilab by WWW - Freemat.infoNo ratings yetArrays - Matrices and Vectors in Matlab, Freemat, Octave and Scilab by WWW - Freemat.info5 pages
- Lap Trinh C - Cao Tuan Dung - Week10 ArraysNo ratings yetLap Trinh C - Cao Tuan Dung - Week10 Arrays11 pages
- Python Tutorial - Slots, Avoiding Dynamically Created AttributesNo ratings yetPython Tutorial - Slots, Avoiding Dynamically Created Attributes1 page
- Python Tutorial - Class vs. Instance AttributesNo ratings yetPython Tutorial - Class vs. Instance Attributes1 page
- CSE-141: Structured Programming CSE-141: Structured ProgrammingNo ratings yetCSE-141: Structured Programming CSE-141: Structured Programming44 pages
- Lesson Plan For First Term 2024/2025 CSC 301 Week 9-10No ratings yetLesson Plan For First Term 2024/2025 CSC 301 Week 9-1010 pages
- O Level m4 r5 Building Iot Applications and C Programming Chapter 4 Download PDF Notes FreeNo ratings yetO Level m4 r5 Building Iot Applications and C Programming Chapter 4 Download PDF Notes Free50 pages
- Module 7 - Part I: 1D Arrays and Lots of BracketsNo ratings yetModule 7 - Part I: 1D Arrays and Lots of Brackets18 pages
- Compare The First Two Elements in The List, Say A (1), and A (2) - If A (2) Is Smaller Than A (1), Then Interchange Their ValuesNo ratings yetCompare The First Two Elements in The List, Say A (1), and A (2) - If A (2) Is Smaller Than A (1), Then Interchange Their Values15 pages
- How To Write Games Using Basic4GL - Part 2No ratings yetHow To Write Games Using Basic4GL - Part 218 pages
- Practical No 1 Array Operations - Implement Programs For 1-d Arrays, Implement Programs For 2-d Arrays.No ratings yetPractical No 1 Array Operations - Implement Programs For 1-d Arrays, Implement Programs For 2-d Arrays.7 pages
- Session 14 Numpy Advanced - Ipynb ColabNo ratings yetSession 14 Numpy Advanced - Ipynb Colab11 pages
- Electronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesNo ratings yetElectronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home Appliances21 pages
- FM Transmitter: Matt Baker Kevin Van DykeNo ratings yetFM Transmitter: Matt Baker Kevin Van Dyke15 pages
- Days Breakfast Lunch: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayNo ratings yetDays Breakfast Lunch: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday2 pages
- 3.1 Arrays - Introduction:: Unit Iii - Arrays and StringsNo ratings yet3.1 Arrays - Introduction:: Unit Iii - Arrays and Strings47 pages
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-6-Cluster Suite Overview-En-USNo ratings yetRed Hat Enterprise Linux-6-Cluster Suite Overview-En-US22 pages
- Linux Essentials Certification Instructor Approved: UsersNo ratings yetLinux Essentials Certification Instructor Approved: Users3 pages
- Computer Network 50 MCQ Question With Answer PDF91% (11)Computer Network 50 MCQ Question With Answer PDF8 pages
- File Handling in C Language - C Language Tutorial - StudytonightNo ratings yetFile Handling in C Language - C Language Tutorial - Studytonight4 pages
- Extensible Connectivity 2.0 Management AgentNo ratings yetExtensible Connectivity 2.0 Management Agent54 pages
- VSP Provisioning Guide For Open SystemsNo ratings yetVSP Provisioning Guide For Open Systems650 pages
- 3D Marine Geometry: Overview of Processing MethodologyNo ratings yet3D Marine Geometry: Overview of Processing Methodology24 pages
- Database Management System: Dr. Neha Gulati University Business School Panjab University100% (1)Database Management System: Dr. Neha Gulati University Business School Panjab University30 pages
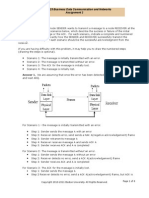
- MET CS 625 Business Data Communication and Networks Assignment 2No ratings yetMET CS 625 Business Data Communication and Networks Assignment 26 pages
- TCP IP Protocol Suite Chap-02 OSI ModelNo ratings yetTCP IP Protocol Suite Chap-02 OSI Model39 pages
- How To Install Endnote X8 and The Accompanying Files in 6 StepsNo ratings yetHow To Install Endnote X8 and The Accompanying Files in 6 Steps5 pages
- CSE370 - Indexing and Hashing (Practice Sheet)No ratings yetCSE370 - Indexing and Hashing (Practice Sheet)11 pages
- Configuring Advanced File Solutions: This Lab Contains The Following Exercises and ActivitiesNo ratings yetConfiguring Advanced File Solutions: This Lab Contains The Following Exercises and Activities16 pages
- 2 Introduction To Data Structures and StackNo ratings yet2 Introduction To Data Structures and Stack24 pages
- Review Questions and Discussion QuestionsNo ratings yetReview Questions and Discussion Questions12 pages