0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views4 pagesPH 5.2 Optimal Use of Drug Therapy - Devices - Storage
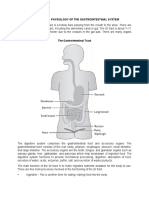
The document outlines a practical session focused on optimal drug therapy, device usage, and medication storage, with specific competencies for communicating with patients. It includes detailed learning objectives for discussing drug effects, adverse effects, usage instructions, device handling, and storage conditions. Additionally, it presents case studies for role play and discussion, emphasizing the importance of patient education and understanding in various medical scenarios.
Uploaded by
beginners4371Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views4 pagesPH 5.2 Optimal Use of Drug Therapy - Devices - Storage
The document outlines a practical session focused on optimal drug therapy, device usage, and medication storage, with specific competencies for communicating with patients. It includes detailed learning objectives for discussing drug effects, adverse effects, usage instructions, device handling, and storage conditions. Additionally, it presents case studies for role play and discussion, emphasizing the importance of patient education and understanding in various medical scenarios.
Uploaded by
beginners4371Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4