0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesWeek 5 Stat Methods and Data Analysis
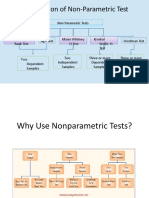
The document outlines statistical tests including t-tests, Wilcoxon signed rank tests, and Hartley tests for hypothesis testing related to population variances. It emphasizes the use of calculators for computing differences and finding p-values, as well as the importance of confidence intervals. Additionally, it notes the conditions under which these tests are applied, such as the handling of ties and the direction of the test statistic.
Uploaded by
aliyahflashCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesWeek 5 Stat Methods and Data Analysis
The document outlines statistical tests including t-tests, Wilcoxon signed rank tests, and Hartley tests for hypothesis testing related to population variances. It emphasizes the use of calculators for computing differences and finding p-values, as well as the importance of confidence intervals. Additionally, it notes the conditions under which these tests are applied, such as the handling of ties and the direction of the test statistic.
Uploaded by
aliyahflashCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2