0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesModule 5
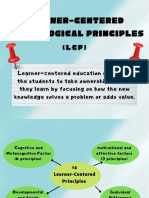
The document outlines the developmental characteristics of school-age children, emphasizing the importance of understanding their cognitive, physical, and social/emotional growth for effective teaching. It highlights that children aged 5 to 8 learn best through hands-on experiences and require engaging lessons, while also noting the varying learning levels and motivations among students. Additionally, it discusses the impact of cultural background on academic performance and the significance of teacher expectations in shaping student outcomes.
Uploaded by
yaserhosainy01Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesModule 5
The document outlines the developmental characteristics of school-age children, emphasizing the importance of understanding their cognitive, physical, and social/emotional growth for effective teaching. It highlights that children aged 5 to 8 learn best through hands-on experiences and require engaging lessons, while also noting the varying learning levels and motivations among students. Additionally, it discusses the impact of cultural background on academic performance and the significance of teacher expectations in shaping student outcomes.
Uploaded by
yaserhosainy01Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2