0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesTP NoSQL
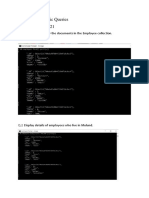
The document provides various MongoDB queries for retrieving restaurant data in Manhattan, focusing on different cuisines, grades, and aggregation techniques. It includes examples of filtering by cuisine type, grade conditions, and using aggregation functions like match, project, and group. Additionally, it demonstrates how to utilize variables for query construction and sorting results.
Uploaded by
boreltidotamekengCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesTP NoSQL
The document provides various MongoDB queries for retrieving restaurant data in Manhattan, focusing on different cuisines, grades, and aggregation techniques. It includes examples of filtering by cuisine type, grade conditions, and using aggregation functions like match, project, and group. Additionally, it demonstrates how to utilize variables for query construction and sorting results.
Uploaded by
boreltidotamekengCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2