0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views6 pagesScience Guided Notes
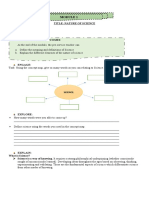
Chapter 1 discusses the nature of science, emphasizing the scientific method as a standardized process for problem-solving and the importance of inquiry in exploring life. It outlines the goals of science, which include providing natural explanations for events and making predictions, as well as the distinction between discovery science and hypothesis-based science. The chapter also addresses the limitations of science, the need for accuracy and error reduction in experiments, and the role of peer review in ensuring scientific validity.
Uploaded by
206296Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views6 pagesScience Guided Notes
Chapter 1 discusses the nature of science, emphasizing the scientific method as a standardized process for problem-solving and the importance of inquiry in exploring life. It outlines the goals of science, which include providing natural explanations for events and making predictions, as well as the distinction between discovery science and hypothesis-based science. The chapter also addresses the limitations of science, the need for accuracy and error reduction in experiments, and the role of peer review in ensuring scientific validity.
Uploaded by
206296Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6