0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views44 pagesSoftware Hacking
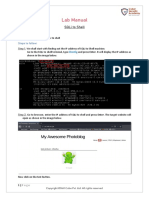
The document discusses software hacking techniques, particularly focusing on how programs can be cracked using assembly debuggers and exploiting vulnerabilities like buffer overflows. It explains the structure of memory, stack operations, and the importance of registers in controlling program execution. Additionally, it covers methods for manipulating applications, including password cracking and bypassing time restrictions in trial software.
Uploaded by
Memoona AsifCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views44 pagesSoftware Hacking
The document discusses software hacking techniques, particularly focusing on how programs can be cracked using assembly debuggers and exploiting vulnerabilities like buffer overflows. It explains the structure of memory, stack operations, and the importance of registers in controlling program execution. Additionally, it covers methods for manipulating applications, including password cracking and bypassing time restrictions in trial software.
Uploaded by
Memoona AsifCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 44