0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views10 pagesCloud Service Models Notes
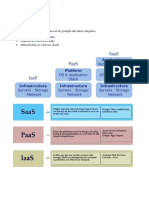
The document outlines the three main cloud service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), detailing their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. SaaS is user-friendly and cost-effective but has limited customization, while PaaS offers development tools for applications with more flexibility, and IaaS provides the most control and customization but requires significant expertise. Each model has unique responsibilities for clients and providers, making them suitable for different organizational needs.
Uploaded by
Dr. Balasubramani RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views10 pagesCloud Service Models Notes
The document outlines the three main cloud service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), detailing their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. SaaS is user-friendly and cost-effective but has limited customization, while PaaS offers development tools for applications with more flexibility, and IaaS provides the most control and customization but requires significant expertise. Each model has unique responsibilities for clients and providers, making them suitable for different organizational needs.
Uploaded by
Dr. Balasubramani RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10