0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pagePhoto Synthe Is
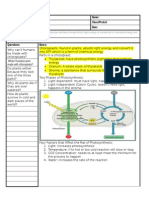
Plants convert light energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis, involving light-dependent reactions that produce ATP and NADPH, and light-independent reactions that convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Enhancing photosynthesis can improve food and fuel production by increasing carbon dioxide concentration, optimizing light intensity, regulating temperature, employing genetic engineering, and utilizing hydroponics. These methods aim to maximize photosynthetic efficiency and crop yield.
Uploaded by
balekenglaronaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pagePhoto Synthe Is
Plants convert light energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis, involving light-dependent reactions that produce ATP and NADPH, and light-independent reactions that convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Enhancing photosynthesis can improve food and fuel production by increasing carbon dioxide concentration, optimizing light intensity, regulating temperature, employing genetic engineering, and utilizing hydroponics. These methods aim to maximize photosynthetic efficiency and crop yield.
Uploaded by
balekenglaronaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1