0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesExercise 9 - Timer and Counter
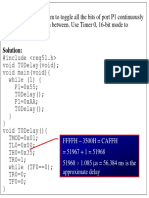
The document outlines an experiment involving the architecture of the 8051 microcontroller, focusing on programming and interfacing applications. It includes aims to write C programs for toggling bits and counting using timers, along with theoretical explanations of timer registers and delay calculations. Additionally, it provides hardware implementation details and a series of exercises to further explore timer functionalities and pulse generation.
Uploaded by
labtophoneCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesExercise 9 - Timer and Counter
The document outlines an experiment involving the architecture of the 8051 microcontroller, focusing on programming and interfacing applications. It includes aims to write C programs for toggling bits and counting using timers, along with theoretical explanations of timer registers and delay calculations. Additionally, it provides hardware implementation details and a series of exercises to further explore timer functionalities and pulse generation.
Uploaded by
labtophoneCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7