0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageJavascript Cheat Sheet
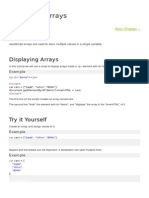
The document explains the basics of arrays and objects in JavaScript, highlighting how arrays can hold multiple data types and how objects store key-value pairs. It covers array methods for editing elements and accessing properties, as well as defining functions and using the return keyword. Examples illustrate the use of dot notation and various array methods, such as push, unshift, shift, and pop.
Uploaded by
Jalal NayanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageJavascript Cheat Sheet
The document explains the basics of arrays and objects in JavaScript, highlighting how arrays can hold multiple data types and how objects store key-value pairs. It covers array methods for editing elements and accessing properties, as well as defining functions and using the return keyword. Examples illustrate the use of dot notation and various array methods, such as push, unshift, shift, and pop.
Uploaded by
Jalal NayanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1