0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views8 pagesFluids - Assignment 1
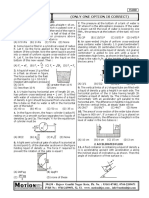
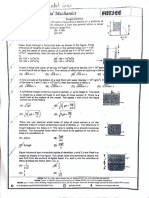
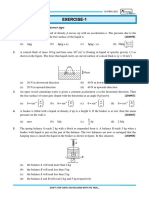
The document is an assignment on the mechanical properties of fluids from Shakthi NEET Academy, containing a series of questions related to fluid mechanics concepts. It covers topics such as buoyancy, pressure, flow rates, and viscosity, with multiple-choice answers provided for each question. The assignment aims to test the understanding of fluid behavior in various scenarios.
Uploaded by
mirumirri7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views8 pagesFluids - Assignment 1
The document is an assignment on the mechanical properties of fluids from Shakthi NEET Academy, containing a series of questions related to fluid mechanics concepts. It covers topics such as buoyancy, pressure, flow rates, and viscosity, with multiple-choice answers provided for each question. The assignment aims to test the understanding of fluid behavior in various scenarios.
Uploaded by
mirumirri7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8