100% found this document useful (1 vote)
138 views16 pagesWavyCurveStandardFunctions PracticeSheetNexus2026
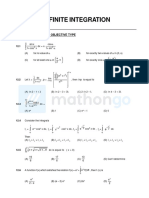
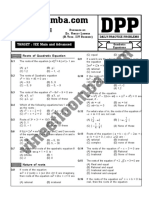
The document contains a series of mathematical problems focused on solving inequalities and determining domains of functions. It includes a variety of questions with multiple-choice answers, covering topics such as quadratic inequalities, logarithmic functions, and greatest integer functions. An answer key is provided at the end, detailing the correct solutions for each question.
Uploaded by
kartikgiri648Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
138 views16 pagesWavyCurveStandardFunctions PracticeSheetNexus2026
The document contains a series of mathematical problems focused on solving inequalities and determining domains of functions. It includes a variety of questions with multiple-choice answers, covering topics such as quadratic inequalities, logarithmic functions, and greatest integer functions. An answer key is provided at the end, detailing the correct solutions for each question.
Uploaded by
kartikgiri648Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16