0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesInheritance
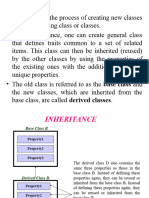
The document provides an overview of inheritance in object-oriented programming, defining it as the process of extending an existing class (base class) into a new class (derived class). It explains what is inherited from the base class, the syntax for implementing inheritance, and the different access control levels (public, protected, private) in inheritance. Several examples illustrate the concepts of inheritance using classes such as Vehicle, Polygon, Car, and Rectangle.
Uploaded by
hfzarjCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesInheritance
The document provides an overview of inheritance in object-oriented programming, defining it as the process of extending an existing class (base class) into a new class (derived class). It explains what is inherited from the base class, the syntax for implementing inheritance, and the different access control levels (public, protected, private) in inheritance. Several examples illustrate the concepts of inheritance using classes such as Vehicle, Polygon, Car, and Rectangle.
Uploaded by
hfzarjCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16