0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesDBMS Assignment 2
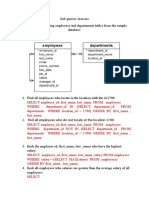
The document outlines a database schema for students and instructors, detailing operations such as adding primary and foreign keys, finding instructors for students, and creating views based on specific criteria. It also includes a second schema for departments and employees, with queries to retrieve employee information based on location, salary comparisons, and department statistics. The document emphasizes the use of various types of joins and subqueries in executing the specified queries.
Uploaded by
try.shreyas25Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesDBMS Assignment 2
The document outlines a database schema for students and instructors, detailing operations such as adding primary and foreign keys, finding instructors for students, and creating views based on specific criteria. It also includes a second schema for departments and employees, with queries to retrieve employee information based on location, salary comparisons, and department statistics. The document emphasizes the use of various types of joins and subqueries in executing the specified queries.
Uploaded by
try.shreyas25Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2