0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views10 pagesCestodes LAB
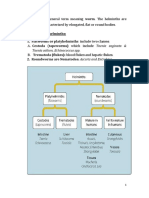
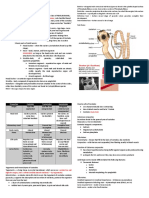
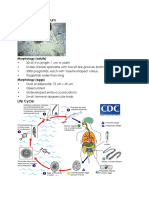
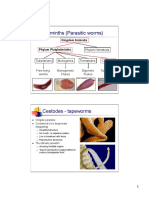
Cestodes, or tapeworms, belong to the class Cestoda and have a flat, ribbon-like body structure with distinct parts including the scolex, neck, and strobila of proglottids. They lack a digestive system and absorb nutrients through their tegument, with various species affecting humans as definitive or intermediate hosts. Notable species include Taenia solium, Taenia saginata, and Echinococcus, each with specific life cycles and associated health risks.
Uploaded by
Janprof FloresCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views10 pagesCestodes LAB
Cestodes, or tapeworms, belong to the class Cestoda and have a flat, ribbon-like body structure with distinct parts including the scolex, neck, and strobila of proglottids. They lack a digestive system and absorb nutrients through their tegument, with various species affecting humans as definitive or intermediate hosts. Notable species include Taenia solium, Taenia saginata, and Echinococcus, each with specific life cycles and associated health risks.
Uploaded by
Janprof FloresCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10