0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views25 pagesMaterial Question
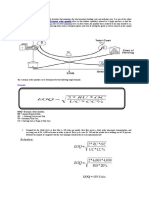
The document contains various problems and solutions related to inventory management, specifically focusing on calculating Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), re-order levels, and stock levels for different materials. It provides detailed calculations and examples for different scenarios, including quantity discounts and varying usage rates. The document serves as a guide for students studying inventory management concepts in a B.Com program.
Uploaded by
umangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views25 pagesMaterial Question
The document contains various problems and solutions related to inventory management, specifically focusing on calculating Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), re-order levels, and stock levels for different materials. It provides detailed calculations and examples for different scenarios, including quantity discounts and varying usage rates. The document serves as a guide for students studying inventory management concepts in a B.Com program.
Uploaded by
umangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 25