0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views33 pages59 Accounts Receivable E Book 2czve6
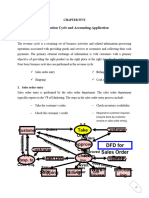
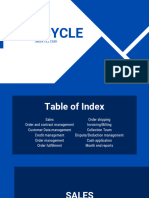
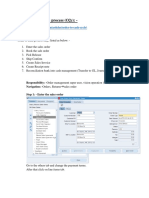
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Order to Cash (O2C) process, detailing its importance in managing customer orders, invoicing, and payment collection. It outlines key components such as order entry, fulfillment, accounts receivable management, and the challenges faced in the O2C cycle. Additionally, it discusses the significance of automation and key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring efficiency and effectiveness in the O2C process.
Uploaded by
singh24rohan2026Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views33 pages59 Accounts Receivable E Book 2czve6
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Order to Cash (O2C) process, detailing its importance in managing customer orders, invoicing, and payment collection. It outlines key components such as order entry, fulfillment, accounts receivable management, and the challenges faced in the O2C cycle. Additionally, it discusses the significance of automation and key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring efficiency and effectiveness in the O2C process.
Uploaded by
singh24rohan2026Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 33