0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views4 pagesK8s Architecture
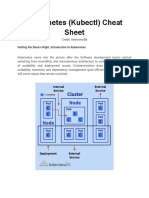
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Kubernetes architecture, including master and worker node components, various Kubernetes objects and workloads, networking, storage, security, cluster maintenance, monitoring, and troubleshooting. It also includes key kubectl commands and syntax for managing resources, along with tips for effective usage and exam preparation. The information is essential for understanding and working with Kubernetes effectively.
Uploaded by
stevicCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views4 pagesK8s Architecture
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Kubernetes architecture, including master and worker node components, various Kubernetes objects and workloads, networking, storage, security, cluster maintenance, monitoring, and troubleshooting. It also includes key kubectl commands and syntax for managing resources, along with tips for effective usage and exam preparation. The information is essential for understanding and working with Kubernetes effectively.
Uploaded by
stevicCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4